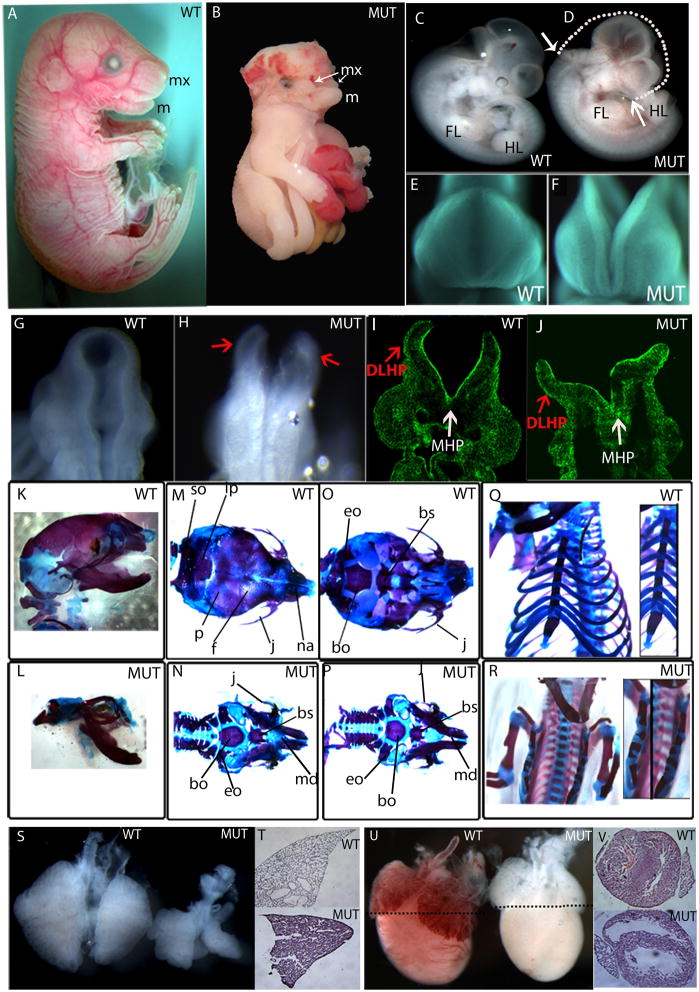
Fig. 2. Grhl2Nisw1 embryos show a general defect in closure of embryonic tissues and lung and heart defects.
(A–J) Wildtype (WT) and homozygous Grhl21Nisw mutant (MUT) embryos show a lack of closure of the neural tube and craniofacial region. Side view of E18.5 embryos (A, B) wildtype and mutant embryos showing the mutant is smaller with hind- to forebrain exencephaly, thoracoabdominoschisis, and soft tissue syndactyly. The mandible (m, lower jaw) is formed in both wild type and mutant embryos, however the maxilla (mx, upper jaw) fails to form properly in the mutant embryos and remains as two separate processes. Side view of E11.5 (C, D) embryos showing similar body size but NTD from hindbrain to forebrain and cleft upper face. White arrows on the mutant show the extent of the neural tube opening, while the white dotted line on the mutant indicates what would be the ~normal shape of the embryo head. Front (E and F) and back (G, H) view of the cranial region of E9.5 embryos showing failure of closure of the facial region and neural tube. (I, J) Section from E9.5 mutant embryo stained with phalloidin, which binds F-actin. Red arrows point to dorsolateral hinge points (DLHP), and white arrows point to medial hinge point (MHP), both of which form in the mutant.
(K–R) Skeletal stainings of E18.5 wildtype and mutant embryos on C3H background. Side (K), top (M), bottom (O) view of the skull and frontal view of the rib cage (Q) of wildtype embryos.
Side (L), top (N), bottom (P) view of the skull and frontal view of the rib cage (R) of mutant embryos.
(S) Wildtype and mutant lungs of E14.5 embryo. (T) H&E staining of E18.5 lung of wildtype and mutant embryos. (U) E18.5 heart of wildtype and mutant embryo. Black dotted lines indicate the level of section shown in (V).
so: supraoccipital, p: parietal, ip: interparietal, f: frontal, j: jugal, na: nasal, eo: exoccipital, bo: basioccipital, bs: basisphenoid.