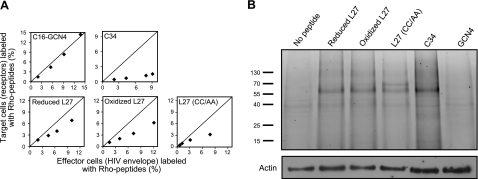
Figure 4.
Loop peptides interact with gp41 and have an enhanced tendency to bind ENV-expressing effector cells. A) Relative binding of Rho-labeled peptides to specific cell populations. In each panel, x axis represents the percentage of effector cells (with HIV ENV) labeled with Rho peptide that was calculated using Eq. 2; y axis represents the percentage of target cells (with receptors) labeled with Rho peptide that was calculated using Eq. 3 (see Materials and Methods). Line in each panel indicates where we would expect the data if there is no preference between the different populations. Different data points represent rising peptide concentrations (up to 1 μM for the L27 peptides and C34; up to 250 nM for the C16-GCN4 peptide). B) Binding of fluorescently labeled peptides to the proteins of coincubated target and effector cells. Unlabeled Jurkat E6-1 and Jurkat HXBc2 cells (2×106) were coincubated in the presence of 2 μM Rho-labeled loop peptides, as well as with 2 μM Rho-labeled control peptides (C34 and GCN4), cross-linked, and lysed. Cell proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE, and proteins bound to fluorescently labeled peptide were detected by measuring the fluorescent signal of Rho. Protein mass (kDa) is indicated at left. Next, the amount of actin in each run was checked by Western blot analysis with anti-actin antibody. Experiments with fluorescent peptides were performed similarly to the cell-cell fusion assay; results shown were obtained from a representative experiment.