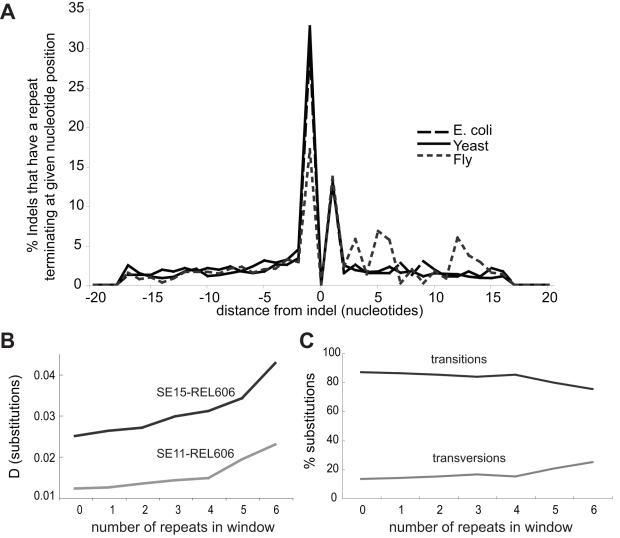
Figure 6. Repeat-rich sequence windows contain increased sequence diversity.
The location of repeat sequences often coincides with indel position in E. coli, S. paradoxus, and Drosophila. Shown are the 20 nucleotides upstream (negative integers) and downstream (positive integers) of the indel (position zero). A repeat is scored once in the nucleotide position in which it terminates, for example, A repeat of four A's running from position −5 to −1 is recorded as a repeat at position −1 (A). Sequence windows from new E. coli alignments not containing indels were binned according to the number of 4 mer homonucleotide repeats they contained. D was found to increase with the increased number of repeats (B), as did the ratio of transversion to transition substitutions (C). The repeat density effect was stronger in a more diverged two-strain comparison (B), indicating that repeats are associated with the accumulation of substitutions over time.