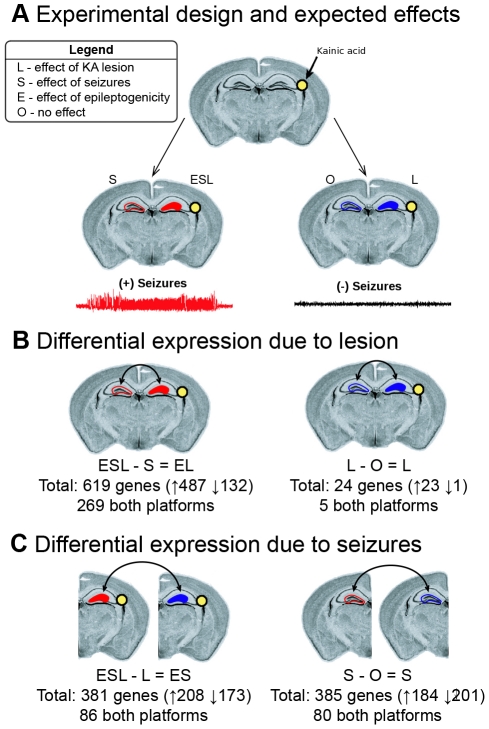
Figure 2. Experimental design and differential expression analysis.
Animals were injected with KA as described in the methods, and gene expression between different samples was compared to identify the effects of seizures and neurotoxic lesion. a) All animals were injected with KA into the right hippocampus but only half of the animals developed chronic epilepsy. Expression in both hippocampi from five animals that developed chronic seizures and five that did not develop chronic seizures was investigated using both the Agilent and Codelink microarrays. The expected effects of interest are illustrated, including 1) the effect of the lesion (L), 2) the effects of seizures (S), and 3) the effects associated with epileptogenicity (E). b) We used two differential expression analyses to identify gene expression changes caused by the lesion. We found 619 differentially expressed genes between the lesioned and non-lesioned hippocampi in animals with seizures (ESL-S = EL) and 24 differentially expressed genes between the lesioned and non-lesioned hippocampi of animals without seizures (L-O = L). c) We then used two differential expression analyses to identify gene expression changes caused by seizures in the lesioned and non-lesioned hippocampi. We identified 381 differentially expressed genes between animals with and without seizures in the lesioned hippocampus (ESL-L) and 385 differentially expressed genes between animals with and without seizures in the non-lesioned hippocampus (S-O).