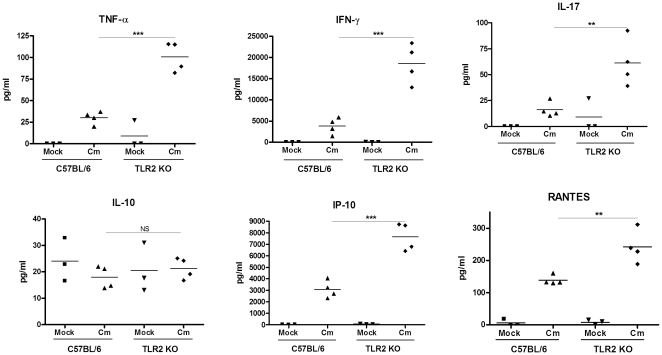
Figure 3. Intranasal infection of TLR2-deficient mice with C. muridarum induces more exaggerated lung inflammatory cytokine response compared to infected wild type mice.
C57BL/6 or TLR2 KO mice on the same background were intranasally inoculated with PBS (mock) or 5×103 IFU/mouse of C. muridarum Nigg, as described in the Methods. At seven days post infection, lung homogenates were assayed for a panel of 22 inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. Shown above are representative results for 6 of the cytokines assayed. Each data point represents one mouse, and the horizontal bar represents the mean. Significance was calculated as follows using a two-tailed t-test: **, p≤0.01 and ***, p≤0.001 for the infected C57BL/6 vs. infected TLR2-deficient mice. NS, not significant. This figure is representative of three independent experiments performed.