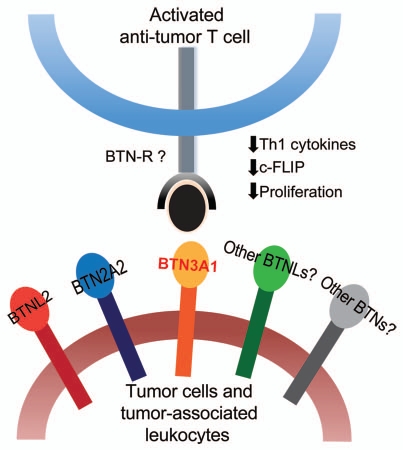
Figure 1.
BTN and BTNL molecules impair T-cell responses. Expression of multiple BTNs and BTNLs by tumor cells or tumor-associated leukocytes may act in concert to potently hinder the function of anti-tumor T cells. BTN3A1, for instance, interacts with a so far unidentified receptor expressed on activated T cells to downregulate anti-apoptotic c-FLIP and abrogate their TCR-induced proliferation. BTN3A1 also inhibits secretion of Th1 cytokines by activated T cells. Future research is aimed at identifying a novel putative T-cell receptor(s) for BTN and BTNL molecules.