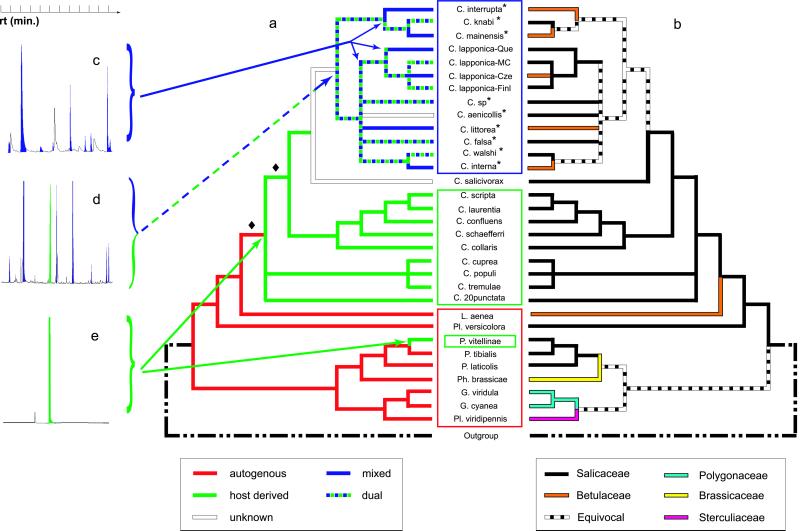
Figure 3.
(a) MP reconstruction of chemical defense strategies on the MP strict consensus from Fig. 1a; red, autogenous monoterpene iridoids; green, salicylaldehyde derived from salicin (sequestered from Salicaceae); blue, mixed metabolism, i.e., butyric acids and esters of them originating from esterification of de novo-synthesized butyric acids by alcohols taken up from the food plant. Some taxa within the interrupta lineage have a dual defense combining the mixed and host-derived metabolisms. (b) MP reconstruction of host plant associations. Que, Queyras (France); MC, Massif Central (France); Cze, Czech Republic; Finl, Finland. Asterisks indicate North American species within the interrupta group. (c–e) Typical gas chromatograms characterizing, mixed-metabolism, dual, and host-derived defenses, respectively; blue peaks, butyric acids and esters of them; green peak, salicylaldehyde; rt, retention time. The low bootstrap support for the two nodes indicated by a diamond do not challenge the general pattern of chemical defense evolution uncovered here (see text for details).