Figure 1.
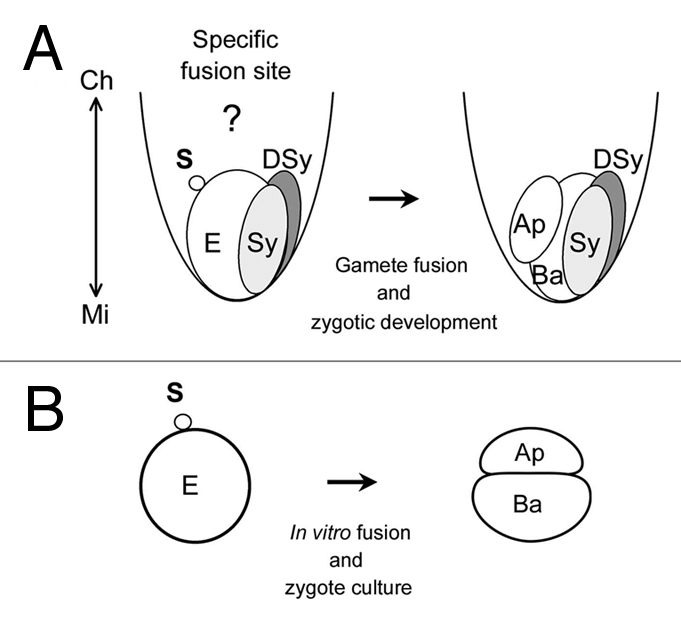
Sperm fusion site on an egg cell and two-celled proembryo embedded in rice embryo sac (A) or produced by in vitro fertilization (IVF) system with rice gametes (B). (A) One of two sperm cells released into an embryo sac fuses with an egg cell. Because the egg and sperm cells exist as hemi-protoplasts and protoplasts in the embryo sac, respectively, to allow gamete fusion, it is possible that gamete fusion can occur around the chalazal surface of the egg cell. After gamete fusion, the zygote divides parallel or slightly oblique to the region facing the synergid and the resulting two-celled embryo comprises a small apical cell with dense cytoplasm and a larger vacuolated basal cell.25 The double arrowed line shows the chalazal-micropylar axis. (B) the zygote produced by IVF divides into an asymmetric two-celled embryo consisting of a small apical cell with dense cytoplasm and a large basal cell with well-developed vacuoles, as in planta. Ap, apical cell; Ba, basal cell; DSy, degenerated synergid; E, egg cell; S, sperm cell; Sy, intact synergid.
