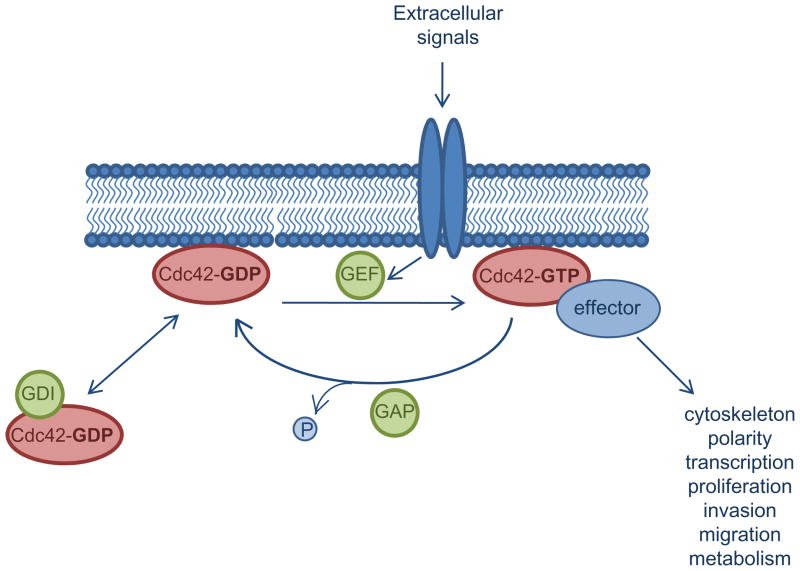
Figure 1. Biochemical regulation of Cdc42 activity by three classes of regulators.
In response to stimulatory signals, activated GEFs catalyze the dissociation of GDP and binding of GTP to Cdc42. In its active, GTP-bound form, Cdc42 binds to effector molecules, leading to the activation of a variety of signaling cascades regulating cellular processes such as proliferation, survival, invasion and migration. GAP proteins enhance the intrinsic GTPase activity of Cdc42, resulting in GTP hydrolysis and inactivation of Cdc42. Cdc42 activity is further inhibited by GDIs which sequester Cdc42 away from cell membranes, thus preventing its activation.