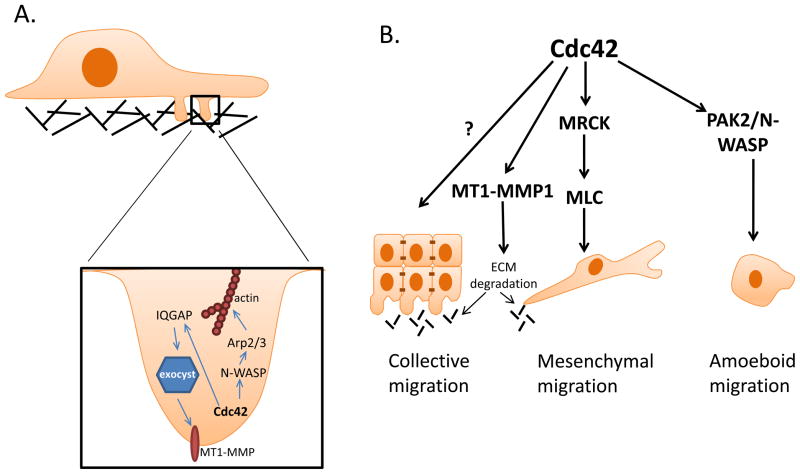
Figure 4. Cdc42 activation contributes to tumor cell invasion and migration.
Cdc42 activation promotes cancer cell invasion through the regulation of invadopodia formation (A). Via its activity in mediating actin polymerization through N-WASP-Arp2/3 complex, Cdc42 promotes invadopodia structure formation. Additionally, through the IQGAP-mediated regulation of exocyst function, Cdc42 regulates the accumulation of matrix metalloproteinases at the tips of invadopodia, facilitating extracellular matrix degradation. Cdc42 activity is involved in both mesenchymal and amoeboid cell migration, while its ability to regulate MMP-mediated matrix degradation may be important for both mesenchymal and collective cell migration (B).