Fig. 1.
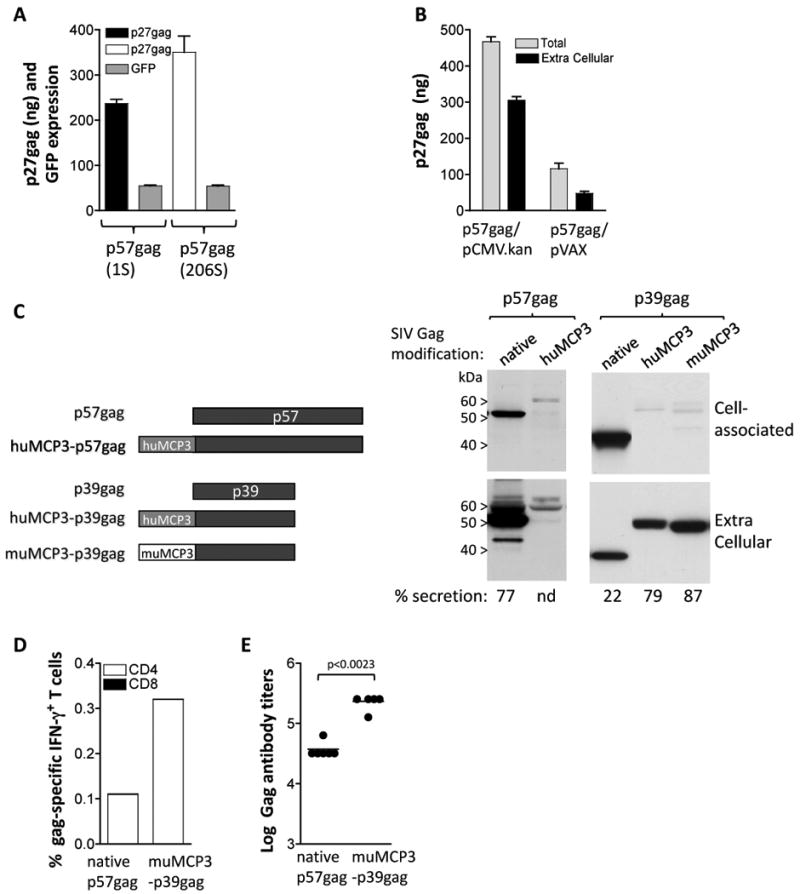
Optimization of SIV Gag expression and immunogenicity in mice. (A) Human 293 cells were transfected in triplicate with 50 ng of gag expression plasmids 1S and 206S and 100 ng of the GFP expression plasmid FRED143. Two days later the cells were harvested and the Gag and GFP levels were measured. Total p27gag (cell-associated and supernatant) and relative GFP values (×100) and SEM are shown. Expression of p57gag from plasmid 206S resulted in 1.5× higher Gag production compared to the levels obtained by plasmid 1S. (B) Comparison of expression of p57gag from the CMV.kan (plasmid 206S) and pVAX plasmids. The two plasmids contain the same p57gag gene including the optimized AUG initiator sequence. HEK 293 cells were transfected with 50 ng of the indicated plasmids and 2 days later Gag expression was measured by antigen capture assay. The mean and SD of triplicate transfection are shown. The mean GFP values (×100) obtained from the cotransfected pFRED143 plasmid are 657 and 740 for p57gag/CMV.kan and p57gag/pVAX, respectively. (C) The cartoon depicts the native p57gag and p39gag and modifications thereof. The fusion proteins comprise the human MCP-3 and p57gag or the p39gag; the murine MCP-3 and p39gag. Plasmids expressing the different forms of Gag were transfected into human 293 cells. The expression vectors producing the native p57gag (plasmid 1S), the fusion of MCP-3 with p57gag (plasmid 214S), p39gag (plasmid 208S), the fusions of human MCP-3 (plasmid 209S) and the murine MCP-3 (plasmid 213S) with p39gag are shown. Human 293 cells were transfected with the p57gag plasmid series or the p39gag plasmid series, respectively, in different experiments. Two days later, the cells were harvested. The Gag proteins from the supernatants (1/250 of sample) and the cell extracts (1/250 of sample) were separated on SDS-PAGE and were visualized on Western immunoblot using pooled antiserum from SIVmac251 infected macaques. Transfection efficiencies were controlled by co-transfection of GFP encoding plasmid pFRED143. The relative GFP values (×100) were 260 and 150 for the p57 plasmid series, and 220, 170 and 160 for the p39 plasmid series respectively. (D) Groups of Balb/c mice (N=6) were immunized with DNA plasmids producing the native p57gag (plasmid 1S) or the murine MCP3-p39gag (plasmid 171S) at day 0 and week 4 and were sacrificed 2 weeks later. Gag-specific cellular immune responses were analyzed in pooled splenocytes by flow cytometric analysis. (E) The endpoint titers of the Gag-specific binding antibody from the mice that received the plasmids described in panel B were determined by ELISA from individual serial 4-fold diluted plasma samples. Statistical analysis was performed using two-tailed Mann Whitney t test.
