Fig. 2.
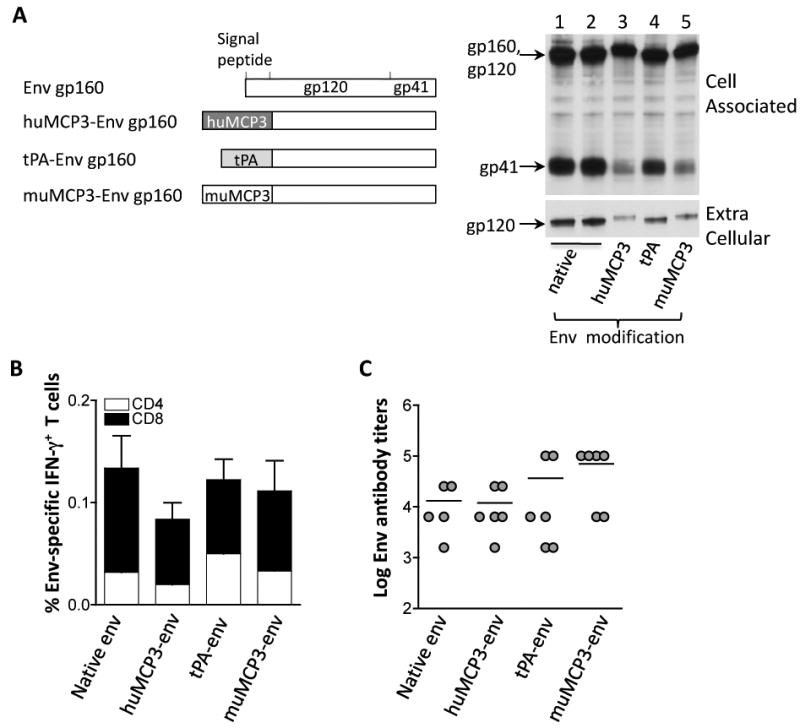
Immunogenicity of native and modified SIV Env proteins in mice. (A) The cartoon depicts the native gp160env as well as the modified gp160env proteins which have the native signal peptide replaced by the human or murine MCP-3 chemokine or the tPA signal peptide. Human 293 cells were transfected with 100 ng of the plasmids expressing the native gp160env (plasmid 64S, lane 1; plasmid 99S, lane 2); the modified gp160env proteins with the native signal peptide replaced by the human (plasmid 73S, lane 3) or murine MCP-3 (plasmid 115S, lane 5) chemokine or the tPA signal peptide (plasmid 78S; lane 4). Two days later, the cells were harvested and 1/250 of the supernatants and cell extracts, respectively, were visualized by Western immunoblot analysis using pooled antiserum from SIVmac251 infected macaques. Transfection efficiency was controlled by co-transfection of GFP encoding plasmid pFRED143. The relative GFP values (× 100) obtained from lanes 1-5 were: 30, 40, 110, 100 and 50, respectively. (B) Immunogenicity of Env produced from the indicated plasmids was assessed. Groups of Balb/C mice (N=5-6) received the plasmids expressing the native (plasmid 64S), the human MCP3-env (plasmid 73S) or murine MCP3-env (plasmid 115S) or the tPA-env (plasmid 78S). The mice were vaccinated 3 times (day 0, week 3 and week 6) and were sacrificed 2 weeks later. Env-specific cellular immune responses were analyzed from splenocytes of individual mice and provided as mean and standard error (SEM) of IFN-γ-producing CD4+ and CD8+T cells. (C) The endpoint titers of the Env-specific binding antibody from the individual mice described in panel B were determined by ELISA from serial 4-fold dilutions of individual plasma samples. The mean titers are indicated.
