Figure 1.
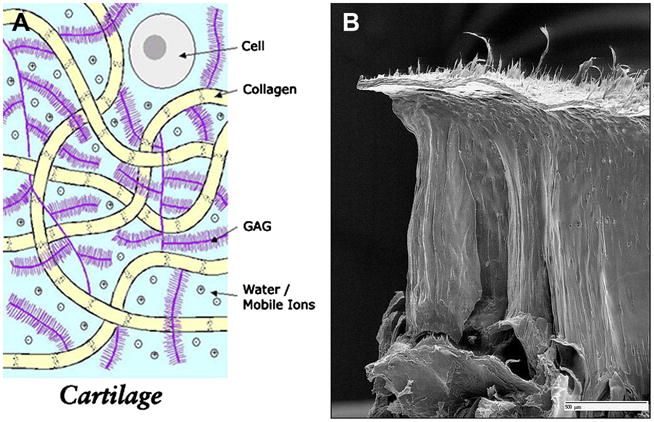
Figure 1A. Cartilage is mostly acellular and avascular, and has a limited ability to heal. The extracellular matrix consists of water, collagen, and glycosaminoglycan. Several aggrecan molecules are attached to a central core fiber filament of hyaluronic acid, to which the aggrecan monomers are bound through a linking protein. A large number of carboxyl and sulfate residues on the GAG side chains are ionized under physiologic conditions and impart a negative charge density (Courtesy of Deb Burstein, BIDMC).
1B. The collagen fibers have a unique zonal architecture as shown here on this freeze fracture image, with superficial, tangential, radial, and calcified zones (courtesy of Doug Goodwin MD).
