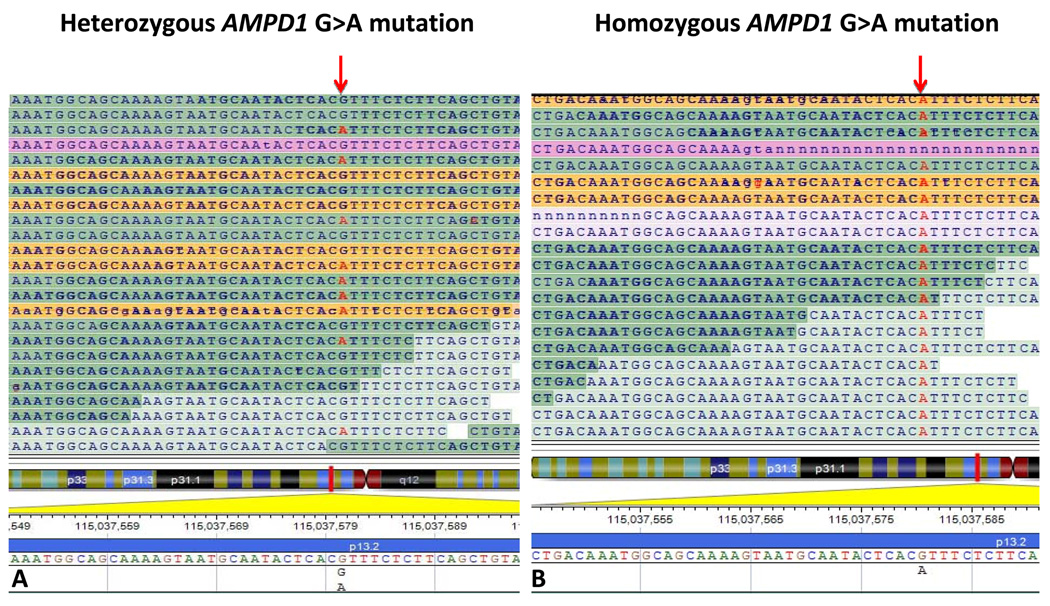
Figure 4. Detection of single nucleotide variant by whole-exome sequencing.
Panel A illustrates an example of sequence output (anti-sense strand) of a NGS machine from a family member heterozygous for G>A (c.C34T, p.Q12X) mutation in AMPD1. Panel B represents a sequence read out from another family member who is homozygous for the mutation and has skeletal myopathy. The homozygous p.Q12X mutation leads to skeletal myopathy due to AMPD deficiency, which was confirmed biochemically. An arrow indicates the mutation.