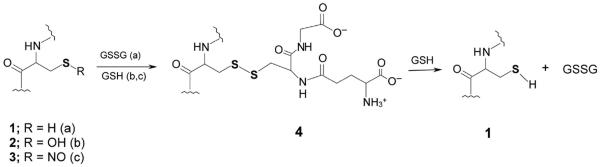
Figure 1. Some reactions leading to reversible glutathionylation of proteins and peptides involving a reducible mixed disulfide.
When the GSSG/GSH ratio is favorable, an oxidizable cysteine residue in protein (1) (R = H) may react with GSSG to generate the mixed disulfide (4, PSG, pathway a) and GSH. On the other hand, if the cysteine residue is oxidized to a sulfenic acid (2, R = OH), the protein may react with a GSH equivalent to generate the mixed disulfide (4, pathway b). In another case, the nitrosated cysteine residue (3) (R = NO) may react with GSH to form the mixed disulfide (4, pathway c) and HNO. The mixed disulfide can be converted back to the reduced form (1) by GSH with the formation of GSSG. Note that the mixed disulfide (4) can also be formed from reaction of 1 with GSNO, GSO or GS(O)SG (9). Note that the sulfur atoms are shown bolded for emphasis.