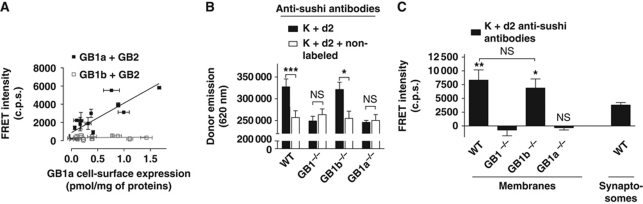
Figure 2.
Detection of GABAB tetramers on brain membrane. (A) FRET intensity measured using Lumi4-Tb (K) and d2-conjugated monoclonal anti-sushi antibodies on COS-7 cells expressing increasing amounts of GB1a and GB2 (black squares) or GB1b and GB2 (open squares). The background signal was determined in the absence of d2-conjugated antibodies. Cell-surface expression was measured by binding assay. (B) Specific K anti-sushi antibody labelling on brain membrane prepared from wild-type, and GB1−/−, GB1a−/− or GB1b−/− mice determined in the presence of d2 anti-sushi antibodies with (white bars) or without (black bars) an excess of non-conjugated anti-sushi antibodies. The specific antibody labelling for each condition tested is given by the difference between the black and the white bars. (C) FRET intensity between K and d2-conjugated anti-sushi antibodies measured on brain membrane prepared from wild-type, GB1b−/−, GB1a−/− or GB1b−/− mice or on synaptosomes prepared from wild-type mice. The background signal was determined on samples labelled with K and an optimized amount of non-conjugated antibodies to obtain the same donor emission as in the assay (data not shown). Data in (A–C) are mean±s.e.m. of three individual experiments each performed in triplicates. *, ** and *** represent P<0.05, P<0.01 and P<0.001, respectively, in a paired t-test; in (C) samples were compared with GB1−/−.