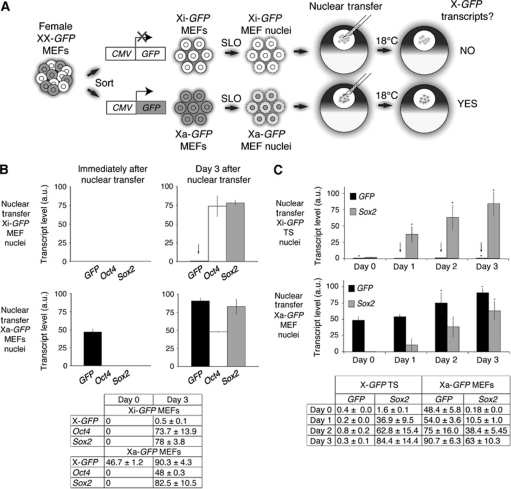
Figure 1.
The inactive X chromosome of differentiated somatic cells is remarkably resistant to reprogramming by Xenopus oocytes. (A) Nuclear transfer experimental scheme. Female MEFs with an X-linked CMV-GFP transgene on the active (Xa) or on the inactive (Xi) X chromosome were sorted, permeabilized with Streptolysin O (SLO) and the resulting nuclei transplanted into the germinal vesicles (GVs) of stage V Xenopus oocytes. Transplanted oocytes were incubated at 18°C and samples were collected at several time points for transcriptional analysis. Transcriptional reactivation of X-GFP was assayed by qRT–PCR. (B) The Xi of MEFs is resistant to transcriptional reprogramming by oocytes. qRT–PCR analysis of GFP (black), Oct4 (white) and Sox2 (grey) expression in transplanted nuclei immediately and 3 days after nuclear transfer. The arrow highlights maintenance of Xi-GFP repression. P<0.05, n=3, error bars are mean±s.d. The table shows transcript levels mean±s.d. a.u. represents arbitrary unit. (C) The imprinted Xi of trophoblast stem (TS) cells is resistant to transcriptional reprogramming by oocytes. Quantitative analysis of GFP (black) and Sox2 (grey) expression in transplanted Xi-GFP TS and Xa-GFP MEFs nuclei. Arrows highlight maintenance of imprinted Xi-GFP silencing. P<0.05 for GFP, except samples marked *P<0.06. For Sox2, P<0.05, except samples marked *P<0.1, n=3, error bars are mean±s.d. The table shows transcript levels mean±s.d. a.u. represents arbitrary unit.