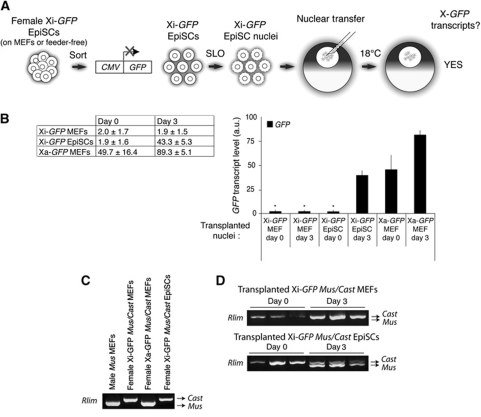
Figure 2.
The Xi of EpiSCs can be reactivated by nuclear transfer to Xenopus oocytes. (A) Schematic representation of Xi-GFP EpiSCs nuclear transfer experiments. Undifferentiated female EpiSCs cultured on feeders were sorted from differentiating cells by flow cytometry of SSEA1-positive, GFP-negative EpiSCs. After SLO permeabilization, Xi-GFP EpiSC nuclei were transplanted to oocyte GV, and the resulting oocytes were cultured for 3 days. (B) Xi-GFP of EpiSC nuclei can be reactivated after nuclear transfer. Quantitative RT–PCR of X-GFP expression after nuclear transfer. Time points and types of transplanted nuclei are indicated. Transcript levels are shown in table±s.e.m. P<0.05, except samples marked *P<0.2, n=3, error bars show s.e.m. a.u. represents arbitrary unit. (C) Rlim allele-specific RT–PCR. Validation of allele-specific Rlim RT–PCR on cells derived from embryos resulting from a cross between X-GFP Musculus and Castaneus mice (maternal genotype denoted first). MEFs and EpiSCs were derived from embryos genotyped for sex (Ube1 expression) and X-GFP transgene expression and sorted by flow cytometry based on GFP expression. (D) Rlim can be reactivated after nuclear transfer. Allele-specific Rlim RT–PCR of Xi-GFP mus/cast MEFs and EpiSCs, immediately after (day 0) or on day 3 after nuclear transfer.