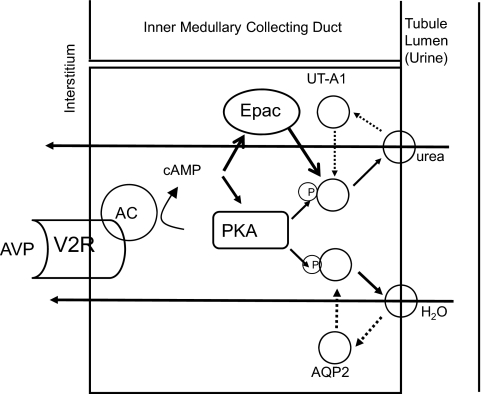
Fig. 3.
Urea and water reabsorption in principal cells of the inner medullary collecting duct. For water, vasopressin (AVP) binds to the V2-receptor (V2R) on the basolateral plasma membrane, activates adenylyl cyclase (AC), increases intracellular cyclic AMP (cAMP), and stimulates protein kinase A (PKA) activity. Cytoplasmic vesicles carrying the AQP2 water-channel protein are phosphorylated and inserted into the luminal membrane in response to vasopressin, thereby increasing the water permeability of this membrane (45). When vasopressin stimulation ends, water channels are retrieved by an endocytic process, and water permeability returns to its low basal rate. The process is similar for urea, except that cAMP stimulates both PKA and Epac, the exchange protein activated by cAMP (31, 33). UT-A1 is ubiquitinated and degraded in the proteasome (46). Although not shown, the basolateral plasma membrane contains AQP3 and AQP4 water channels and the UT-A3 urea transporter, thereby completing the transcellular pathways for water and urea reabsorption.