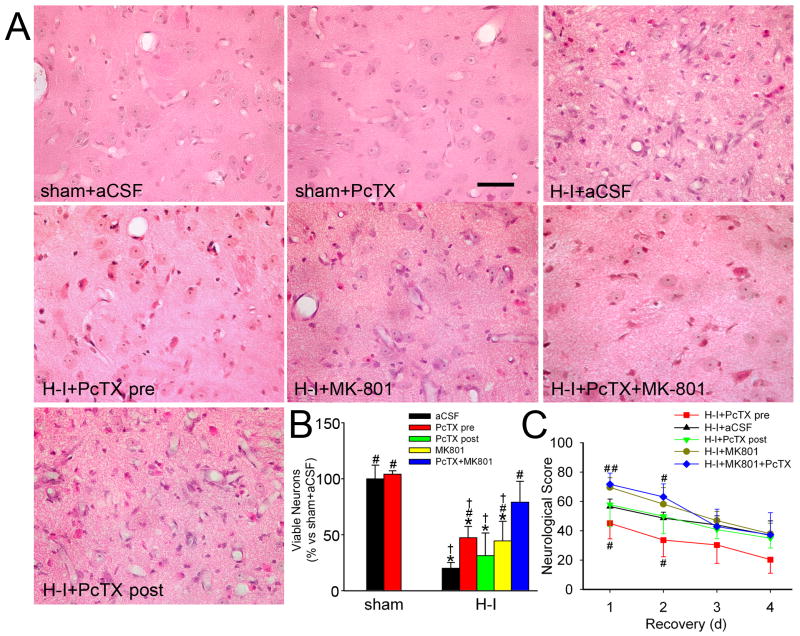
Figure 3.
Effects of PcTX on neuronal damage and neurologic deficits in piglets subjected to H-I. Piglets exposed to H-I or sham surgery received aCSF, PcTX pretreatment, PcTX post-treatment, MK-801, or PcTX and MK-801 in combination. (A) Representative photographs of H&E-stained sections at 4 days of recovery show normal cellular morphology and cytoarchitecture in putamen of sham-operated animals treated with aCSF and PcTX. All H-I groups contained putaminal neurons that exhibited ischemic morphology (cytoplasmic microvacuolation, eosinophilia, and nuclear pyknosis) or that had lost distinct structure. Scale bar = 40 μm. (B) Quantitative results for viable putamen neurons (expressed as a percentage of the mean value of the sham+aCSF group). (C) Neurologic scores during the 4-day recovery. Data are shown as means ± SD (n = 4 to 8 per group). *P < 0.05 versus sham-operated aCSF group; #P < 0.05 versus H-I aCSF group; † P < 0.05 versus H-I PcTX+MK-801group; ANOVA followed by the Student-Newman-Keuls test. H-I+PcTX pre, H-I piglets pretreated with PcTX; H-I+PcTX post, H-I piglets post-treated with PcTX.