Figure 2.
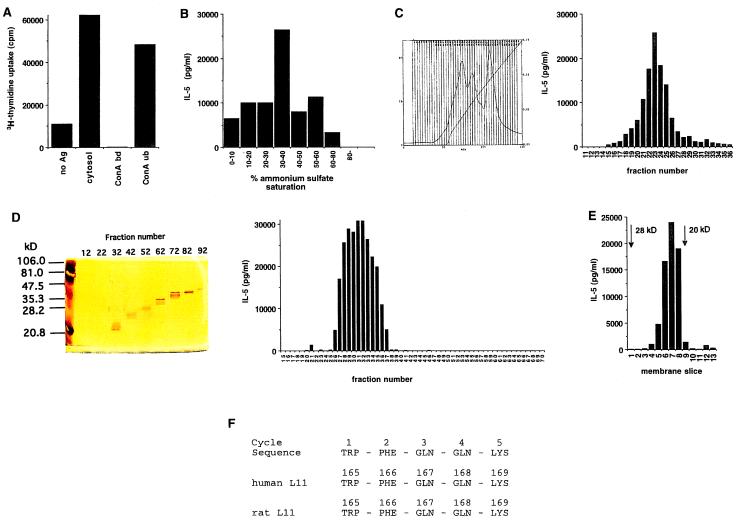
Purification and identification of the antigen recognized by TML-01 and 24D3. (A) Meth A lysates (30 ml cytosol derived from a ≈15-ml cell pellet) were fractionated by Con A-agarose affinity chromatography, and the bound and unbound fractions were assayed for antigenic activity, as described in Materials and Methods. (B) Con A-unbound proteins were fractionated by increasing saturation with ammonium sulfate, and each fraction was tested for antigenic activity. The proteins precipitating between 30% and 40% saturation were found to be the most active. This fraction was solubilized in 20 mM of sodium phosphate buffer and was resolved by DEAE-agarose chromatography by elution through a 0–1 M NaCl gradient on BIOCAD (C). The curved line shows absorbance at a wavelength of 280 nm, and the straight line depicts the shape of the salt gradient as conductivity. Each fraction (10 μl of 3 ml) was tested for antigenic activity. Fraction 24 was found to be the most active. (D) Fractions 22–24 of C were pooled and concentrated to 500 μl by Centricon 10, loaded onto a Mini Prep Cell, and separated on a 12% SDS gel at 200 V for 6 h. Proteins were eluted at 500 μl for 3 min per fraction. Each fraction (10 μl) of the preparative gel was tested for antigenic activity. Activity was present in fractions 27–36, which were smaller than 28 kDa. (E) Fractions 28–33 of the preparative gel in D were pooled, concentrated, and loaded onto a 12% SDS/PAGE gel. The proteins were transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane, which was cut into 1-mm slices. The slices were placed in culture with CD4+ T cells and splenic APCs. Activity was measured by IL-5 release in the supernatant. Activity was present in the fractions corresponding to a ≈21- to 22-kDa band. (F) The nitrocellulose slice corresponding to the active fraction in E was subjected to digestion with trypsin and Edman degradation (Keck Facility of Yale University). One of the fragments showed a signal through the first five cycles (F). This sequence was identical to the sequence of ribosomal protein L11 of rats and humans.