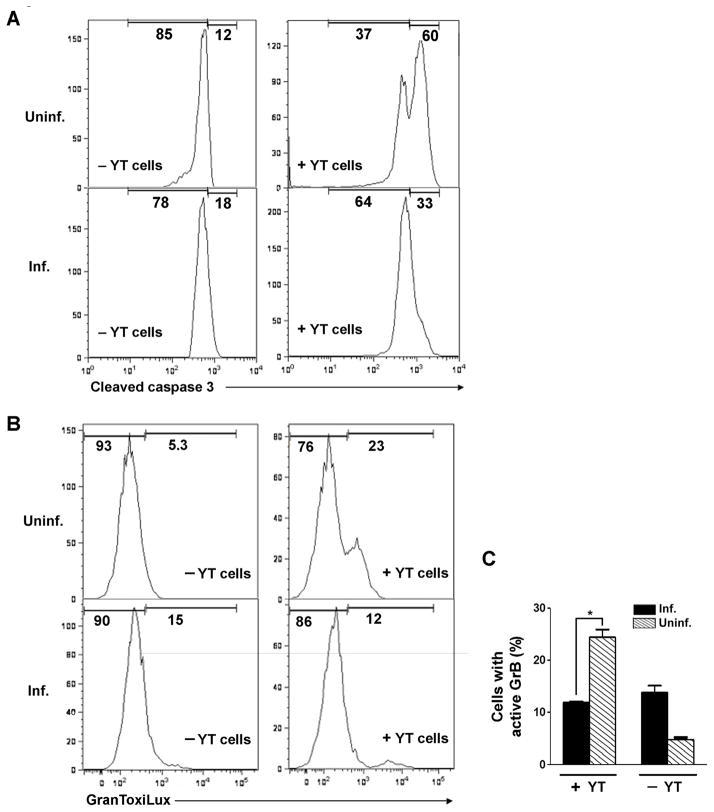
Fig. 10.
Toxoplasma gondii inhibits granzyme B (GrB) activity and apoptosis induced by cytotoxic lymphocytes. (A) Inhibition of apoptosis. HeLa cells, infected with T. gondii expressing yellow fluorescent protein at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 4 for 16 h, were co-cultured for 6 h with YT-1 effector lymphocytes, rinsed to remove effector cells, and processed for detection of caspase-3 cleavage by flow cytometry. Uninfected (Uninf.) and infected (Inf.) fractions of the same culture were compared; the frequency of infection was 54%. (B) Inhibition of GrB activity. Jurkat cells, infected with T. gondii expressing mCherry at a MOI of 1 for 16 h and stained with Hoechst 33342, were co-cultured for 1 h with YT-1 cells, incubated 1 h in GranToxiLux, and analyzed for GranToxiLux cleavage by flow cytometry. Uninf. and inf. fractions of the same culture were compared; the frequency of infection was 40%. (C) Quantitation of the experiment shown in (B). * P = 0.01 by Student’s t test (n = 4). The data in the figure are representative of two experiments.