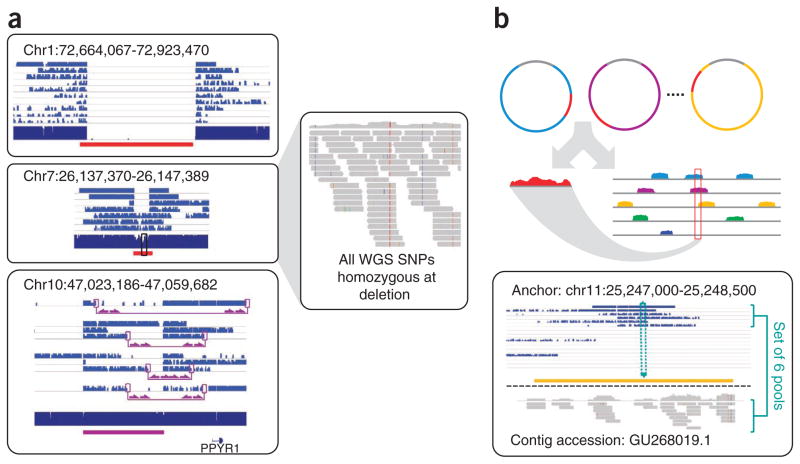
Figure 4.
Insertion anchoring and structural variation detection. (a) Homozygous deletion (top), hemizygous deletion (middle) and inversion (bottom) with fosmid clone support. Deletion calls were made using read depth and paired-read discordance. Inversions were called by paired-read discordance. SNPs within hemizygous deletions appear as stretches of hemizygosity by whole-genome shotgun sequencing. Purple connections indicate the additional support of strand discordance of read pairs spanning genomic DNA and the vector backbone. (b) Novel contigs not present in the reference assembly (red) but detected among clone pool–derived reads (light blue, purple, yellow) are anchored by searching for positions in the reference common to those pools but missing from most or all other pools. This approach anchors 1,733 recently reported insertion sequences7,8 including contig GU268019.