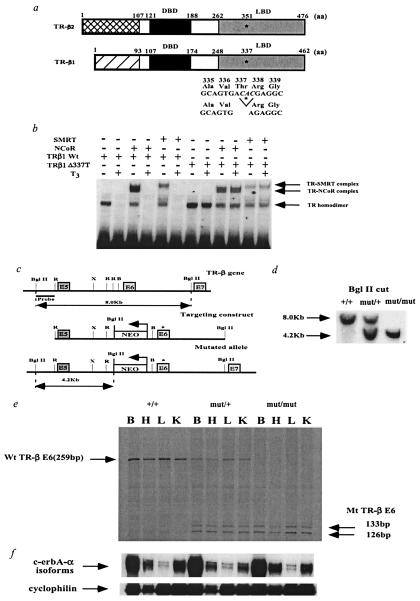
Figure 1.
Functional properties of the human mutation Δ337T and generation of TR-β knock-in mice by introduction of the human mutation Δ337T into the mouse TR-β locus. (a) Schematic representation of the TR-β isoforms and location of the Δ337T mutation in the mouse. Amino acid numbering is given for the human mutation in the mouse TR-β locus. Because this mutation is present in the ligand-binding domain (LBD), the mutation is present in both TR-β isoforms. DBD, DNA binding domain. (b) Gel mobility shift assay showing that the human Δ337T receptor mutant constitutively binds to corepressors (N-CoR, SMRT). T3 was added at a concentration of 100 nM. (c) Introduction of Δ337T mutation into the mouse TR-β gene by homologous recombination. The asterisk marks the position of the Δ337T mutation in exon 6 (E6). The neomycin resistance gene (NEO), driven by the phosphoglycerate kinase promoter (bent arrow), was inserted into intron 5 in a direction opposite that of transcription as indicated. R, EcoRI; X, XbaI; B, BamHI. (d) Homologous integration of the targeting vector was confirmed by Southern blot analysis of genomic DNA digested with BglII and probed with an α-32P-labeled BglII-EcoRI probe located outside of the targeting vector. (e) Expression of the wt and mutant TR-β alleles in transgenic mice. RNase protection assays in various tissues were performed with a mouse exon 6 riboprobe. In mut/+ and mut/mut animals, the Δ337T mutation is located in the middle of exon 6. RNase treatment in these animals cleaved the probe into two smaller fragments (133 and 126 bps). Ten micrograms of total RNA from brain (B), heart (H), liver (L), and kidney (K) of 3-week-old male mice was analyzed. Because of the similar size of the control cyclophilin probe, it was hybridized to the same samples in a separate RNase protection assay. No significant differences were noted among these samples (data not shown). (f) RNase protection assay examining TR α1 with cyclophilin as a control. An N-terminal c-erbA-α probe was used in an RNase protection assay with cyclophilin as a control. Ten micrograms of total RNA from brain (B), heart (H), liver (L), and kidney (K) of 3-week-old male mice was analyzed. TR expression (β and α1) in the cerebellum was similar to that in whole brain (B) as shown in Fig. 1 e and f (data not shown).