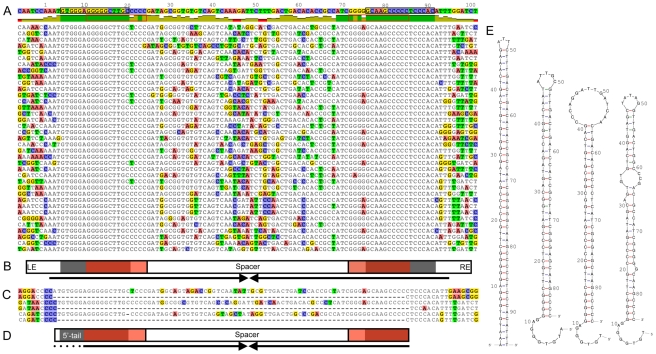
Figure 4. General organization and predicted secondary structure of REPINs.
(A) Alignment of 101 GI REP doublets forming hairpins (REPINs) from SBW25 (37 are shown) shows a symmetrical (palindromic) organization comprised of two highly conserved regions separated by a spacer. Top line shows the consensus sequence followed by a graph displaying identity to the consensus (green denotes 100% identity). Two invariant regions of 16 bp are found in the left and right ends (LE, RE). These sequences are organized as inverted repeats and define the most abundant 16-mer in the SBW25 genome (black box). Each 16-mer overlaps a GI REP sequence (red box). (B) General REPIN features including LE and RE, each comprised of a highly conserved 16-mer (black) overlapping a REP sequence (red), with the two ends separated by a spacer. For a GI doublet the distance between the first residues of the two invariant 16-mers is 71 bp. Complementary bases permit formation of a hairpin structure (arrows). (C) Three excision events detected from Illumina sequencing reads reveal a putative transposition intermediate. Full-length sequences show three genomic regions located between 2,577,312–2,577,231, 3,857,520–3,857,439 and 5,683,545–5,683,624 bp on the SBW25 genome, each of which contains a REPIN. The partial sequences below each genomic region are Illumina reads from which the REPIN has been excised (see also Figure S6). (D) Cartoon of the excised region indicating putative transposition intermediate. Note the 5′-tail, which generates an asymmetrical sequence. (E) Secondary structure prediction for the consensus GI REPIN shows that the conserved bases on each side can pair resulting in a long hairpin (E, left). Predictions for transposition intermediates in the same order as the alignments in (C): the second, third and fourth hairpin correspond to the first, second and third alignment. The single stranded 5′-tail is free to pair with a complementary sequence.