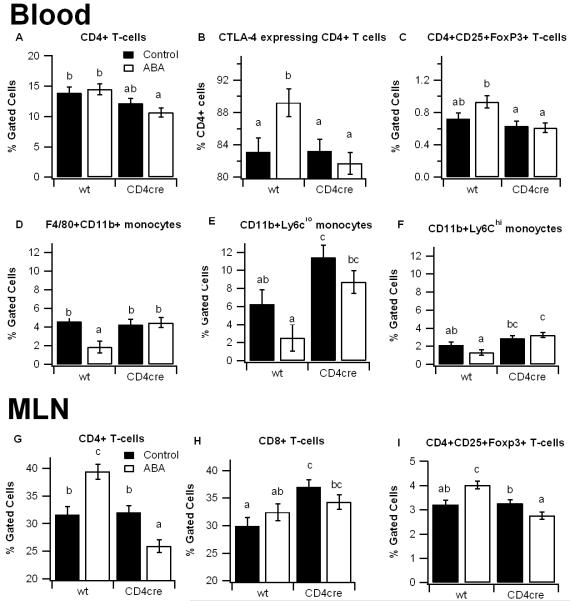
Figure 3.
Effect of dietary abscisic acid (ABA) supplementation on lymphocyte subsets in PPAR γ-expressing and T cell-specific PPAR γ null mice. PPAR γ flfl;CD4 Cre− (wt) and PPAR γ flfl; CD4 Cre+ (CD4cre) mice were fed ABA-supplemented (100 mg/kg) or control diets for 35 days and challenged with 2.5% dextran sodium sulfate (DSS) for 7 days. Blood (A-C) and MLN (D-E) were immunophenotyped with anti-CD3, anti-CD4, anti-CD8, anti-CTLA4, anti-FoxP3, anti-F4/80, and anti-CD11b mouse monoclonal antibodies and the immune cell populations were analyzed by flow cytometry with FACS diva software. Data are represented as mean ± standard error. Statistically significant differences (P<0.05) between groups are indicated with an asterisk (n=8 mice/group) in three independent experiments.