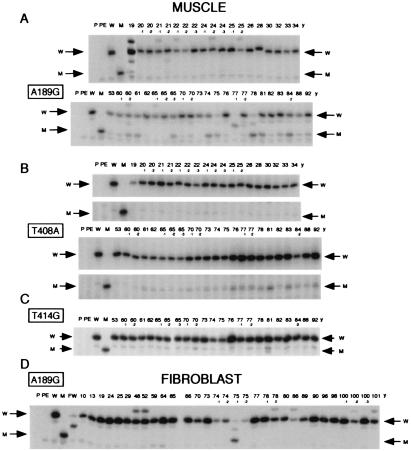
Figure 2.
Autoradiograms showing the electrophoretic patterns obtained in the analysis of different mutations by allele-specific termination of primer extension. (A) Detection of the A189G mutation in DLP4 segments PCR-amplified from muscle mtDNA of individuals without any history of neuromuscular disease (group A, see Materials and Methods), comparing 19 individuals aged 19 to 34 years and 23 individuals aged 53 to 92 years old. (B) Detection of the T408A mutation in DLP6 segments amplified from muscle mtDNA of the individuals indicated in A. A section of the gel has been cut out for space considerations. The extended primer, which terminated at the site of the mutation, corresponds to the lower band of each doublet (indicated by M arrow), whereas the upper band is a spurious product visible also in the lane for the wild-type DLP6 (W). (C) Detection of the T414G mutation in DLP6 fragments amplified from muscle mtDNA of the individuals indicated in A. (D) Detection of the A189G mutation in DLP4 segments amplified from fibroblast mtDNA of 32 individuals from 20-week fetal (FW) to 101 years old. In A and D, some samples exhibited consistently in repeated runs a relatively minor band migrating slower than the extended primer terminated on the wild-type template (W), which, most likely, resulted from a conformational change in the template associated with a polymorphism(s) in DLP4; this hypothesis is supported by the sequencing data for individuals 22 y-1 and 25 y-2 (data not shown), for 79 y (Table 1), and for 48 y (1), and by the presence of the same band in multiple tissues from 79 y and 90 y (see below, Fig. 3). In A, C, and D, the weak abnormal bands migrating faster than the mutant or wild-type band, but which were present also in the PE lane and/or W lane (see below), were due to spurious products. In the lanes for 19 y, 21 y, 60 y-2, 75 y, 77 y-1, 77 y-2, and 78 y of A and in the lanes for FW and 75 y-1 of D, a band [migrating approximately mid-way between the extension product corresponding to the wild-type sequence (terminating at position 187) and that corresponding to the mutant sequence (terminating at position 189)] represents the extended primer prematurely terminated on the wild-type template, due presumably to an A to G transition at position 188. The number above each lane represents the age of the individual analyzed. P, primer; PE, primer + Sequenase; W and M, primer extension products obtained on plasmid DNA carrying a cloned DLP4 or DLP6 fragment with wild-type and, respectively, mutant sequence.