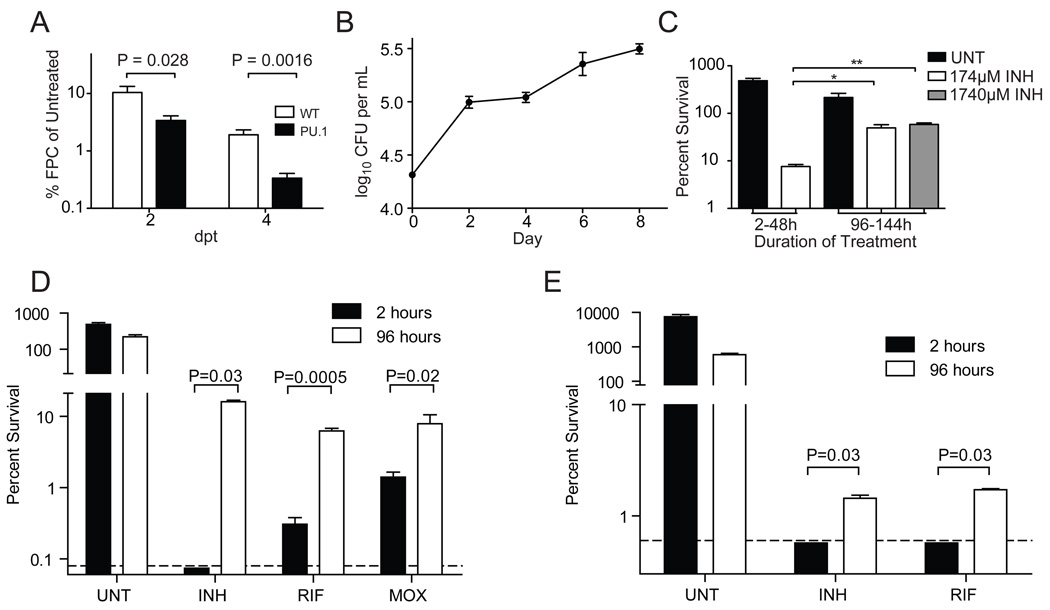
Figure 4. Antibiotic tolerance is induced by macrophage residence.
A) Wild-type and PU.1-morphant larvae were infected with 300 Mm. One dpi, larvae were treated with 290 µM INH, or left untreated. Larvae were imaged at two and four dpt and bacterial burdens determined by FPC. For each timepoint, FPC of each treated larva was normalized to the mean FPC of the untreated control group. N=20 wild-type or 12 PU.1 morphant larvae per group. P values determined using Student’s t-test.
(B and C) J774A.1 macrophages we re infected with Mm and were left untreated, or were treated with INH prior to lysis and enumeration of CFU. (B) Growth of Mm in the untreated control wells. (C) Survival of intracellular Mm upon exposure to 174 or 1740 µM INH during the time periods indicated (two-48 hours, or 96–144 hours) prior to macrophage lysis and enumeration of CFU. Percent survival was compared using one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post-test.
(D) Mm were used to infect THP-1 macrophages for 2 or 96 hours prior to being released by macrophage lysis. CFU were enumerated at the time of release, and again following 48 hours exposure to 174 µM INH, 1.21 µM RIF, 7.48 µM MOX, or left untreated. For the purpose of display, values below the limit of detection (0.08%, dashed line) were arbitrarily set to 0.074%. P values were determined using Student’s t-test (RIF and MOX), or the Mann-Whitney rank test (INH).
(E) Mtb strain H37Rv was used to infect J774A.1 macrophages, and were grown and treated as described for (D), except that the concentration of INH was 4.4 µM, reflecting the greater inherent susceptibility of this organism to INH. For the purpose of display, values below the limit of detection (0.6%, dashed line) were arbitrarily set to 0.57%. P values were determined using the Mann-Whitney rank test. In all panels, error bars represent SEM.