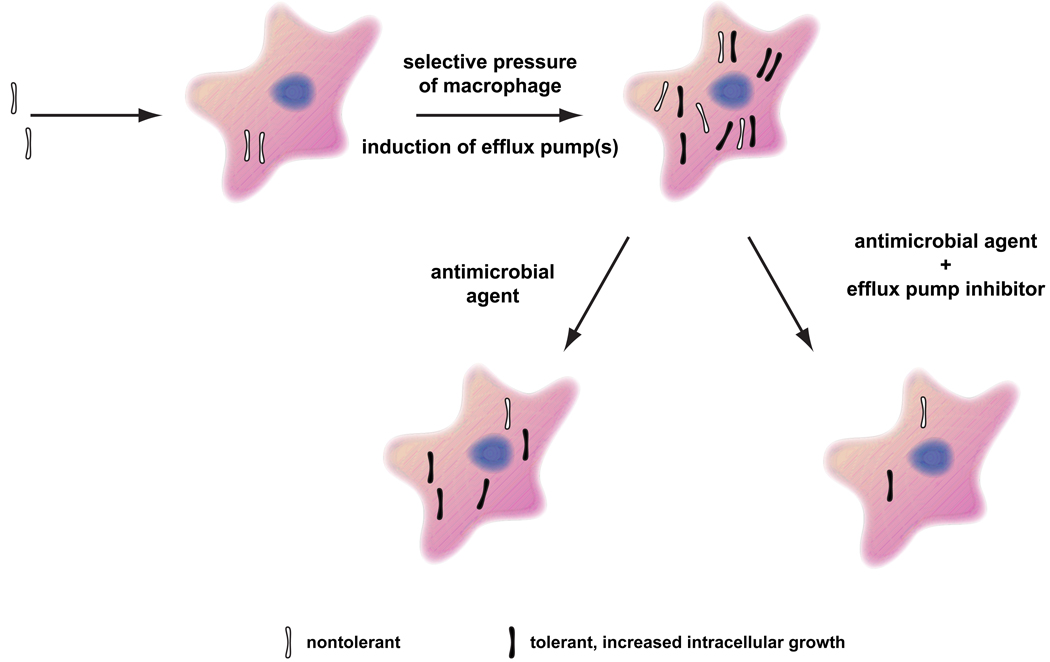
Figure 7. Model for the mechanism of antibiotic tolerance in TB and its treatment.
Nontolerant bacteria are phagocytosed by macrophages soon after infection wherein they induce efflux pumps to counter macrophage defenses. These efflux pumps render bacteria tolerant to multiple antitubercular drugs. The tolerant bacteria are associated with the growing population because of their enhanced ability to counter macrophage defenses. Antitubercular drug treatment spares tolerant bacteria and the addition of efflux pump inhibitors reduces their numbers.