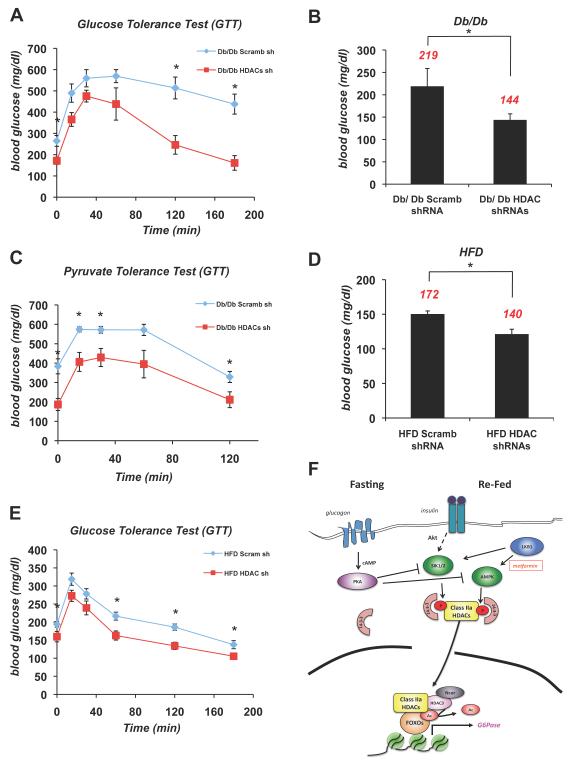
Figure 7. Suppression of Class IIa HDACs Lowers Blood Glucose in Mouse Models of Metabolic Disease.
(A) Glucose tolerance test was performed on db/db mice infected with either scramble (scramb) shRNA or HDAC4/5/7 (HDAC) shRNAs. (n=5) *p<0.02
(B) Db/db mice knocked down with (scramb) shRNA or HDAC4/5/7 (HDAC) shRNAs in liver. 5 days later, mice were fasted for 18h and blood glucose was measured. Average blood glucose value shown in red. (n=5) *p<0.02
(C) Pyruvate tolerance test performed on db/db mice injected with either scramble (scramb) shRNA or HDAC4/5/7 (HDAC) shRNAs. (n=5) *p<0.04
(D) 7 month old B6 mice on a high fat diet (HFD) were treated as in A. (n=5) *p<0.03
(E) Glucose tolerance test was performed on 7 month old B6 mice on HFD as in C. (n=5) *p<0.02
(F) Model for Glucagon dependent regulation of Class IIa HDACs and FOXO. Under fasting conditions, glucagon induces dephosphorylation and nuclear translocation of Class IIa HDACs. Once nuclear, they associate with the G6Pase and PEPCK promoters and bind to HDAC3-Ncor/SMRT and FOXO1/3, resulting in HDAC3-mediated deacetylation and activation of FOXO. Under fed conditions insulin-dependent activation of the LKB1-dependent kinases SIK1/2 stimulates phosphorylation and cytoplasmic shuttling of Class IIa HDACs. Similarly, following metformin treatment, the LKB1-dependent AMPK activation induces Class IIa HDAC phosphorylation and 14-3-3 binding. In response to glucagon, PKA is activated and directly phosphorylates and inactivates AMPK, SIK1, and SIK2 hence resulting in loss of HDAC phosphorylation. Data are shown as mean +/− s.e.m. using Student’s t-test.
See also Figure S7.