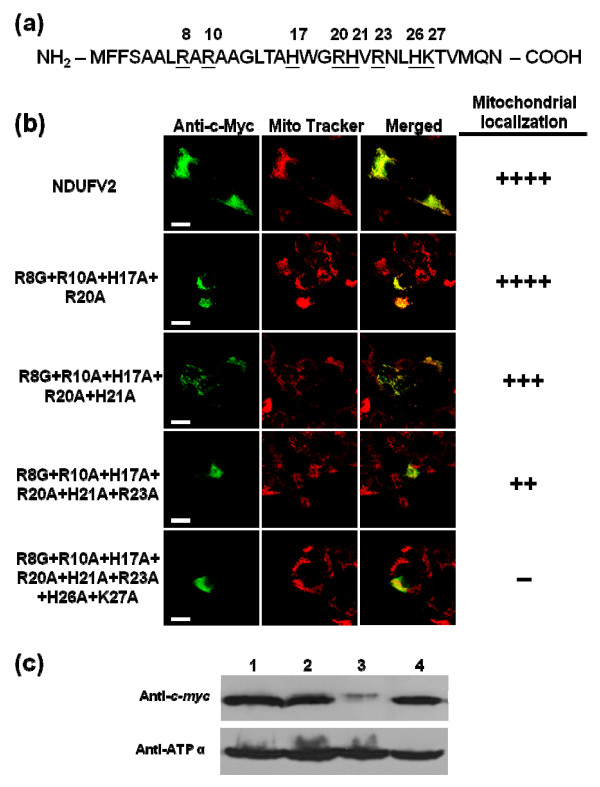
Figure 6.
Effects of basic residue mutation in NDUFV2 MTS on mitochondrial targeting. (a) The sites of basic residue in NDUFV2 N-terminal 1-32 amino acids were underlined and marked. (b) The effect of basic residue mutation within the N-terminal region of NDUFV2 on mitochondrial targeting was evaluated by confocal image analyses. A series of point mutations targeting at arginine, lysine and histidine residues were introduced into NDUFV2 with the c-myc epitope tag and expressed in T-REx-293 cells. The expressed proteins with basic residue mutations were detected by an anti-c-myc-FITC antibody in transfected cells (green color), mitochondria were labeled by Mito Tracker Red (red color), and colocalization of expressed protein and mitochondria is shown as a merged image and indicated by yellow signals. The number of (+) symbols indicates that the proportion of cells exhibiting FITC fluorescence have a typical punctuated staining pattern and mitochondrial colocalization. The (++++) symbol indicates all of the FITC fluorescence signals in transfected cells are fully colocalized with mitochondria. The (-) symbol indicates that there is no cell producing FITC fluorescence within the mitochondrial compartment. Scale bars = 10 μm. (c) The effect of basic residue mutation on mitochondrial targeting was investigated using subcellular fractionation and Western blotting analyses. Western blotting analyses were conducted using mitochondrial extracts from T-REx-293 cells transiently transfected with the wild-type (lane 1), quintuple mutant (R8G+R10A+H17A+R20A+H21A, lane 2), sextuple mutant (R8G+R10A+H17A+R20A+H21A+R23A, lane 3) or NDUFV2 R23A single-pointed mutant (R23A, lane 4) construct. The expressed proteins were detected by an anti-c-myc antibody. ATP synthase subunit α (ATP α) was used as a mitochondrial marker.