Table 2. A comparison of the jackknife success rates by Gnec-mPLoc
[11] and the current iLoc-Gneg on the benchmark dataset 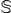 (cf. Supporting Information S1) that covers 8 location sites of Gram-negative bacterial proteins in which none of the proteins included has
(cf. Supporting Information S1) that covers 8 location sites of Gram-negative bacterial proteins in which none of the proteins included has 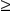 25% pairwise sequence identity to any other in a same location.
25% pairwise sequence identity to any other in a same location.
| Code | Subcellular location | Success rate by jackknife test | |
| Gneg-mPLoca | iLoc-Gnegb | ||
| 1 | Cell inner membrane | 525/557 = 94.3% | 539/557 = 96.8% |
| 2 | Cell outer membrane | 105/124 = 84.7% | 103/124 = 83.1% |
| 3 | Cytoplasm | 357/410 = 87.1% | 367/410 = 89.5% |
| 4 | Extracellular | 79/133 = 59.4% | 115/133 = 86.5% |
| 5 | Fimbrium | 28/32 = 87.5% | 30/32 = 93.8% |
| 6 | Flagellum | 0/12 = 0.0% | 12/12 = 100% |
| 7 | Nucleoid | 0/8 = 0.0% | 4/8 = 50% |
| 8 | Periplasm | 154/180 = 85.6% | 161/180 = 89.4% |
| Overallc | 1248/1456 = 85.7% | 1331/1456 = 91.4% | |
The predictor from [11].
The predictor proposed in this paper.
Note that instead of 1,392 (the number of total different Gram-positive bacterial proteins), here we use 1,456 (the number of total different locative proteins) for the denominator. This is because some of the Gram-negative bacterial proteins in  may have more than one location site. See footnotes a and b of Table 1 for further explanation.
may have more than one location site. See footnotes a and b of Table 1 for further explanation.
