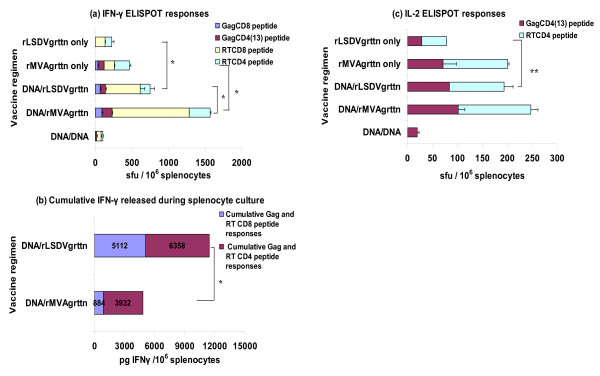
Figure 3.
HIV-specific T cell responses to a DNA vaccine prime and boost with rLSDV-grttn or rMVA-grttn. Groups of mice were vaccinated with the DNA vaccine pVRC-grttn then boosted on day 28 with the DNA vaccine, rLSDV-grttn or rMVA-grttn. Two other groups of mice were vaccinated on day 28 with rLSDV-grttn or rMVA-grttn. Mice in all the groups were killed on day 40, 12 days after the final immunization. Splenocytes, pooled from 5 mice per group, were used in the immunological assays. (a) IFN-γ ELISPOT assay with Gag and RT CD8 and CD4 peptides. Bars are the mean ± the SD of spot forming unit (sfu) from triplicate reactions for 106 splenocytes after subtraction of background spots in the absence of peptide. (b), splenocytes were also cultured with the individual HIV CD8+ and CD4+ T cell peptides for 48 h and culture supernatants were collected and IFN-γ (pg cytokine/106 splenocytes) content quantified. The sum of IFN-γ produced during stimulation with the individual CD8+ and CD4+ T cell peptides was calculated and is presented as the cumulative total IFN-γ produced by HIV-specific CD8+ T cells or CD4+ T cells, values are indicated on the bars; and (c) IL-2 ELISPOT assay with pooled splenocytes and peptides as used in the IFN-γ ELISPOT assay. *: p < 0.01; **: p < 0.05. Data are from a representative experiment.