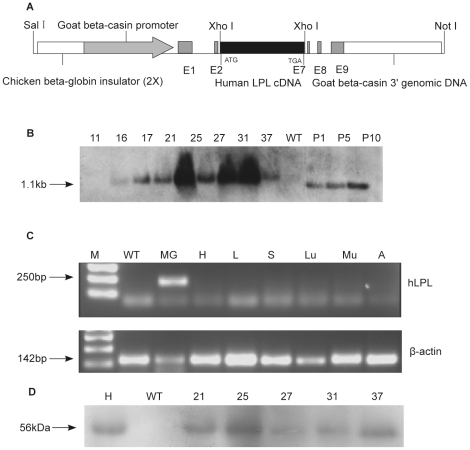
Figure 1. Generation and molecular characterization of transgenic mice.
(A) hLPL cDNA (3.3 kb) was inserted into a backbone isolated from pBC1 using Not I/Sal I. The backbone included 2× chicken β-globin insulator, goat β-casein promoter, untranslated exons E1, parts of E2 and 7, E8, E9 and β-casein 3′ genomic DNA. hLPL cDNA was located between E2 and E7, flanked by two Xho I restriction sites. The translation initiation and termination sites are indicated as ATG and TGA. (B) Southern blot identification of transgenic mice. Digested genomic DNA of eight transgenic founders and WT mice hybridized with a 1.1 kb PCR labeled hLPL cDNA. An expected 1.1 kb band was detected in transgenic samples. WT, wild type mouse genomic DNA. P1, P5, P10 represent 1, 5 and 10 copies of hLPL cDNA plasmid, respectively. (C) RT-PCR analysis of hLPL expression in transgenic mice. All tissue RNAs used for RT-PCR were collected during the middle of the lactation period. Mouse β-actin was used as the RT-PCR internal control. M, 1 kb ladder; WT, wild type mouse mammary gland; MG, transgenic mouse mammary gland; H, heart; L, liver; S, spleen; Lu, lung; Mu, muscle; A, adipose tissue. (D) Western blot analysis of hLPL expression in milk of transgenic mice. The milk samples were collected during the middle of the lactation period, separated by SDS-PAGE and then transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. WT, milk from wild type mice (negative control); H, human milk (positive control); milk from transgenic founders numbered hLPL-21, -25, -27,-31 and -37.