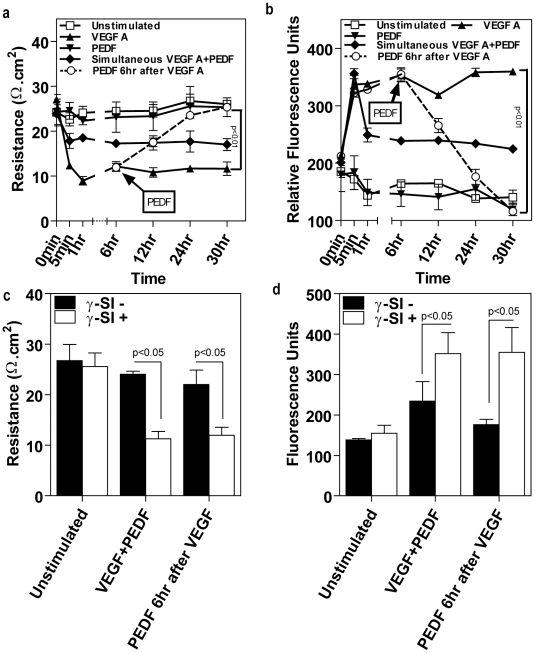
Figure 1. PEDF blocks microvascular endothelial permeability via a γ-secretase dependent mechanism.
(a) Temporal changes in transendothelial resistance across a microvascular endothelial monolayer grown on a Transwell insert treated with vehicle (unstimulated), VEGFA alone, PEDF alone, simultaneous VEGFA+PEDF, PEDF 6 hours post VEGF (n = 4 independent experiments). VEGFA and PEDF were used at 100 ng/ml. (b) Paracellular macromolecular permeability to 40 kDa Dextran-FITC using the conditions described in (A) (n = 4). In the case of PEDF 6 hours post VEGF, Transwell inserts were transferred to new wells containing basal medium without fluorescent dextran. (c) and (d) The effect of γ-secretase inhibitor (γ-SI) on PEDF reduction of VEGF-induced endothelial permeability; (c) TER, (d) paracellular flux. γ-secretase inhibitors were used at 1 nM and data is shown for L685485. Data are represented as means (n = 4) ± SEM.