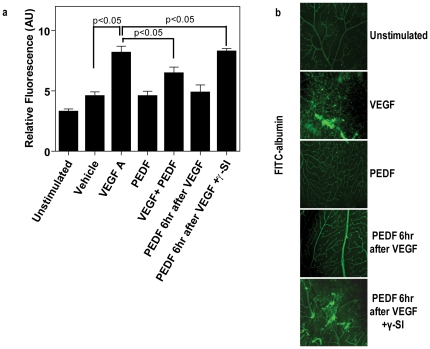
Figure 4. PEDF blocks VEGF-induced retinal vascular permeability in mice.
C57BL/6 mice received intravitreal injections of vehicle (unstimulated), VEGFA alone, PEDF alone, simultaneous VEGFA+PEDF, PEDF 6 hours post VEGF and PEDF 6 hours post VEGF+γ-secretase inhibitor (γSI) (n = 18 animals per treatment). Test compounds (1 µl per eye were given at the following concentrations, VEGF 80 ng/µl; PEDF (80 ng/µl); L685485 24 ng/µl; DAPT 16 ng/µl. 46 hours post the first injection mice received tail vein injections of FITC-labeled albumin. Uninjected animals acted as the baseline control. (a) 46 hours post the first injection mice received tail vein injections of FITC-labeled albumin and retinas were taken for analysis 2 hours later (n = 10–20 per group). Leakage of systemic FITC-labeled albumin into the retina was assessed by measuring total fluorescence in homogenized retina using a fluorescence plate reader. Control is the baseline fluorescence in untreated animals. Data are represented as means ± SEM. (b) Representative confocal microscopy showing dilated vessels and leakage of FITC-labeled albumin in the retinas of mice treated with vehicle (unstimulated), VEGF, PEDF, PEDF 6 hours post VEGF and PEDF 6 hours post VEGF+γ-secretase inhibitor (γ-SI). Scale bar = 50 µM.