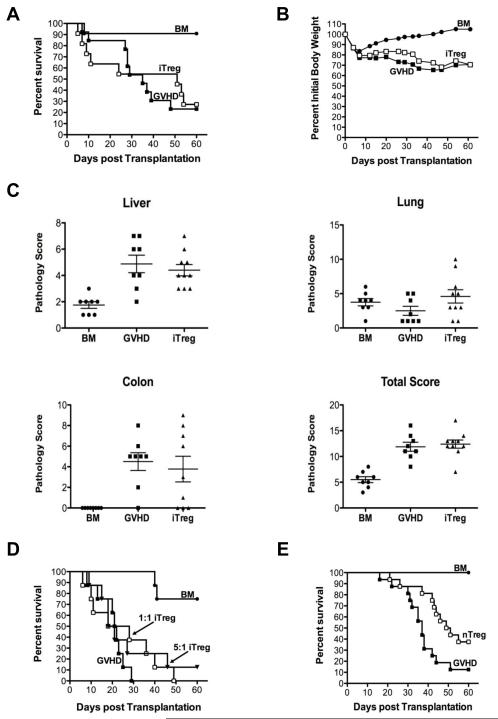
Figure 2. In vitro generated iTregs fail to protect from lethal GVHD.
(A,B). Lethally irradiated (900 cGy) Balb/c mice were transplanted with TCD B6 BM alone (8 × 106) (●, n=11) or together with B6 spleen cells adjusted to yield a T cell dose of 0.4-0.6 × 106 αβ T cells. Animals transplanted with adjunctive spleen cells received either no additional cells (■, n=13) or in vitro-differentiated Tregs in a 1:1 ratio with naïve αβ T cells (□, n=11). Overall survival (A) and the percentage of initial body weight over time (B) are depicted. Data are cumulative results derived from three independent experiments. (C). Pathological damage in the colon, liver, and lung at day 24 post transplantation using a semi-quantitative scale as described in “Histologic analysis.” Mice (n= 8-10/group) were similarly transplanted as in A with the exception that that the αβ T cells dose was 0.5 × 106. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. (D). Lethally irradiated Balb/c mice were transplanted with TCD B6 BM alone (●, n=8) or together with B6 spleen cells adjusted to yield a T cell dose of 0.6 × 106 αβ T cells. Animals transplanted with adjunctive spleen cells received either no additional cells (■, n=8) or in vitro-differentiated Tregs at a 1:1 (□, n= 8) or 5:1 (▼, n= 8) ratio with naïve αβ T cells. Data are cumulative results of two independent experiments. (E). Lethally irradiated Balb/c mice were transplanted with B6 BM alone (●, n=15), or B6 BM plus spleen cells adjusted to yield a dose of 0.6 × 106 αβ T cells. Animals transplanted with adjunctive spleen cells received no additional cells (■, n= 16) or 0.6 × 106 nTregs (□, n= 16). Overall survival is depicted. Data are cumulative results of four experiments. Statistics: * p ≤ 0.05, ** p < 0.01.