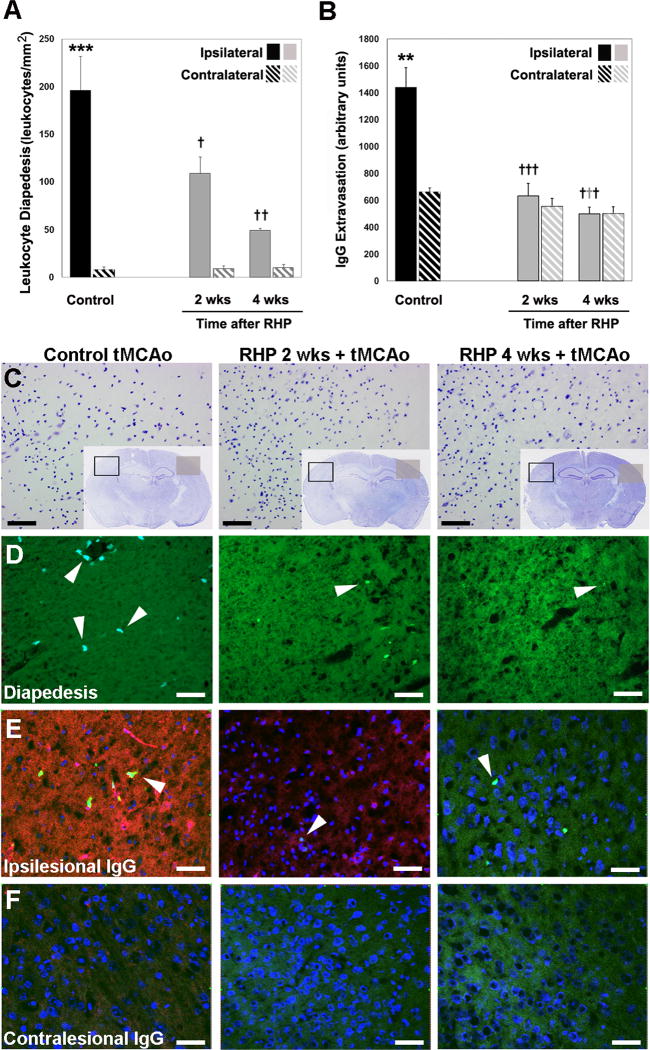
Figure 4.
Repetitive hypoxic preconditioning (RHP) maintains postischemic barrier integrity in LY-EGFP mice. (A,D) Leukocyte diapedesis is increased following transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (tMCAo) in ipsilateral (solid bar) vs. contralateral (hatched bar) hemispheres (n=6; fluorescent leukocytes shown in lower panels by arrowhead from the representative area denoted by a black box in C). RHP, 2 and 4 wks prior to tMCAo, significantly reduced leukocyte diapedesis (n=4,5). (B,E,F) Increased ipsilateral IgG extravasation in controls (solid black) is completely abrogated in animals with RHP. Representative extravasated immunoglobulin G (IgG; red), nuclei (counterstained with ToPro3; blue), and diapedesed leukocytes (arrowheads) shown in (E) the ipsilesional hemisphere from area denoted by a black box in C, and (F) the corresponding contralesional hemisphere from area denoted by the grey square in C. (C) Adjacent cresyl violet stained sections, with an increased magnification (from the black box) of one of the five areas used in quantification. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 vs. contralateral nonischemic hemisphere; †p<0.05, ††p<0.01, †††p<0.001 vs. nonpreconditioned group. Scale bar = 50 μm.