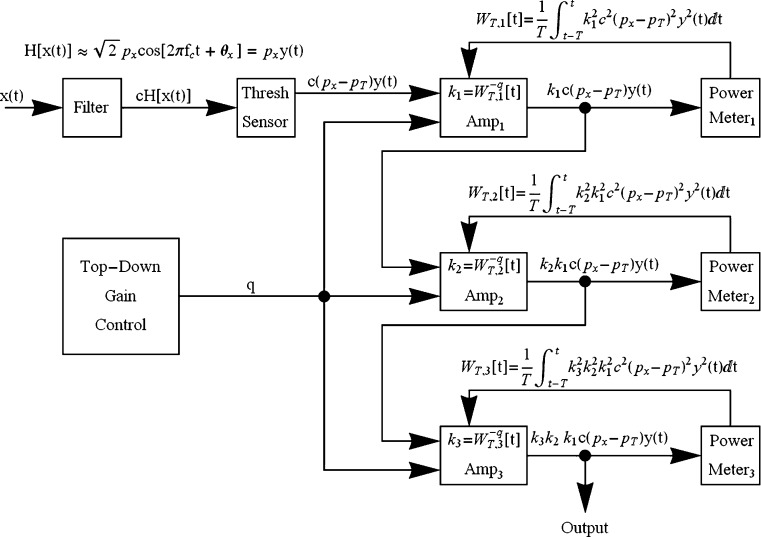
Fig. 10.
The full nonlinear gain-control circuit, after translating the output of the linear filter to its neural equivalent, routes the output to a threshold sensor that passes only the amount of energy in the signal that exceeds some threshold value. The output from the sensor then passes through three concatenated nonlinear amplifiers of the type shown in Fig. 8 to allow for a greater range of compression and more rapid convergence to a steady-state output when the input is a steady-state signal. The amount of feedback is controlled by the parameter q, which is assumed to be under top-down control