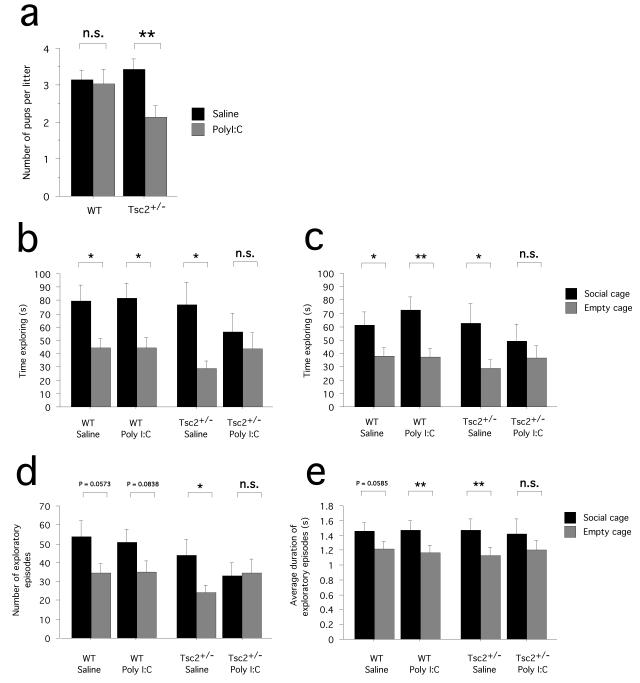
Fig. 2.
Interactive effects of Tsc2 haploinsufficiency and gestational Poly I:C on intrauterine survival and adult social approach behavior. (a) Graph shows the number of pups born in surviving litters, plotted by genotype (Tsc2+/− and WT) and treatment (Poly I:C and saline). Fewer Tsc2+/− pups were born to Poly I:C-injected females compared to saline-injected controls. (b) Graph shows the time (s) spent actively exploring the social cage and the empty cage (sniffing, rearing), as determined by an experienced observer. WT/saline, Tsc2+/−/saline and WT/Poly I:C mice spent significantly more time exploring the social cage than the empty cage, demonstrating normal social approach behavior. Tsc2+/−/Poly I:C mice, in contrast, did not spent more time exploring the social cage than the empty cage. (c,d,e) These graphs show the time spent exploring (c), the number of exploratory episodes (d) and the average duration of exploratory episodes (e) during the social approach behavioral task as quantified with an automated system. While WT/saline, Tsc2+/−/saline and WT/Poly I:C mice tended to show higher values for the social cage than the empty cage, this was not the case for Tsc2+/−/Poly I:C mice. ** P < 0.01, * P < 0.05, n.s. P > 0.05. Data represent means +/− S.E.M.