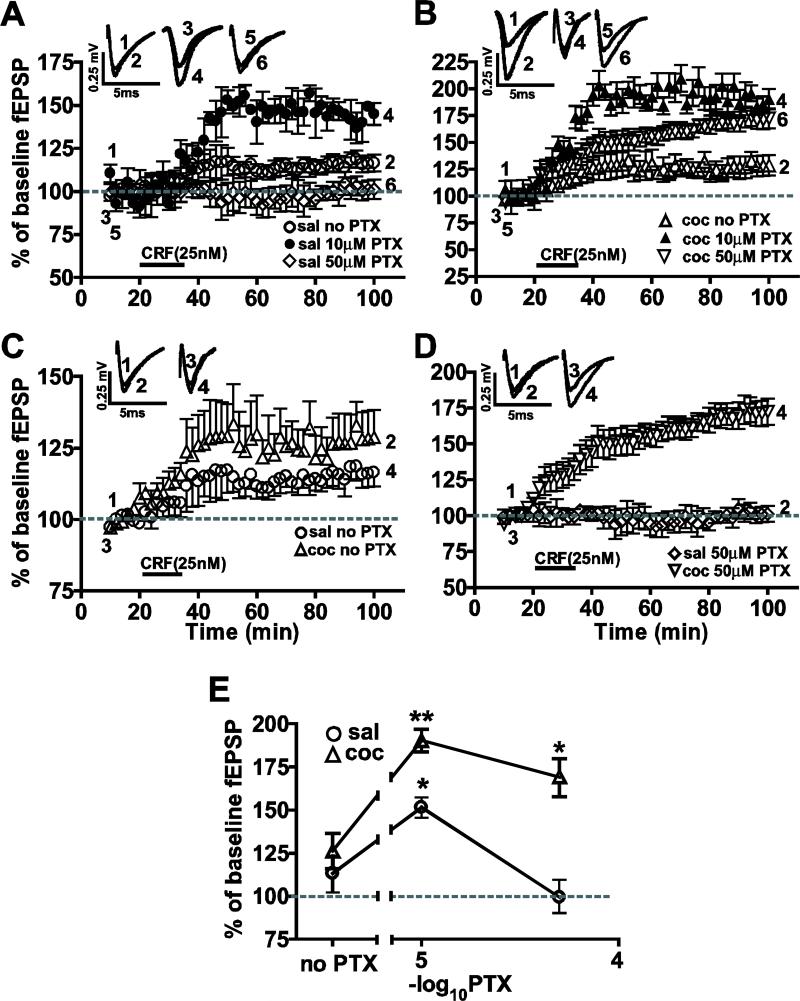
Figure 6.
The enhanced CRF-induced LTP recorded in the cocaine-withdrawn group was dependent on the extent of GABAergic inhibition. (A) Concentration-response relationship for PTX in the saline-treated group showed the greatest potentiation in CRF-induced LTP at 10 μM (filled circles). (B) The enhanced CRF-induced LTP in the cocaine-withdrawn group occurred at 10 (filled triangles) and 50 μM PTX (inverted triangles). (C) Comparing CRF-induced LTP with GABAergic intact (no PTX) in slices showed no difference in CRF-induced LTP in the two treatment groups suggesting removal of inhibition was necessary for the enhanced potentiation after cocaine withdrawal. (D) At 50 μM PTX, an enhanced CRF-induced LTP was recorded in the cocaine withdrawal group (inverted triangle). (E) LTP differences between cocaine-withdrawn and saline-treated groups were measured at 10 μM and 50 μM PTX but not with GABAergic inhibition intact (no PTX).