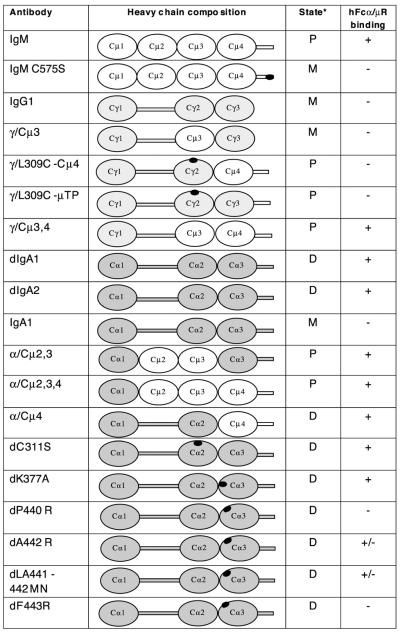
Figure 2.
The nomenclature, heavy chain composition, polymerization state, and hFcα/μR-binding ability of the anti-NIP Ab used in this study. The domain arrangements are shown diagrammatically with heavy chain regions derived from human IgM shown in white, those from human IgG in pale gray, and those from human IgA in dark gray. Hinge regions and tailpieces are shown as bars between domains and C-terminals, respectively. The positions of mutations are indicated by black ovals. Specific details of each mutation have been published elsewhere [8–13]. hFcα/μR-binding data were derived from IFA and/or rosetting experiments. *Predominant polymerization state present: P, polymeric; D, dimeric; M, monomeric.