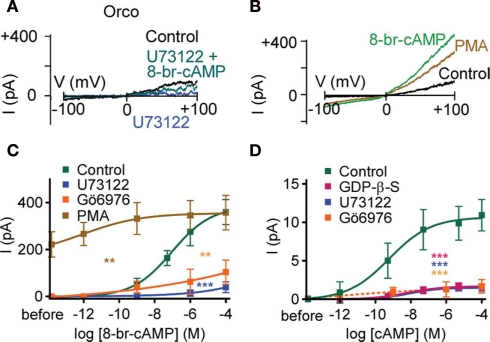
Figure 2.
Phospholipase C and protein kinase C activity regulates the cAMP effect on Orco. (A) Current responses in a HEK293 cell expressing Orco on a voltage ramp from −100 to +100 mV after breaking into the cell (Control), after application of the PLC inhibitor U73122 (10 μM), and after application of 8-br-cAMP (100 μM) in presence of U73122. (B) Current responses in a cell expressing Orco before (Control) and after PMA (1 μM) and 8-br-cAMP stimulation (100 μM). (C) Concentration–response for 8-br-cAMP-induced Orco currents, measured as described in (B) with a standard bath solution (Control) and a solution containing U73122 (10 μM), the PKC inhibitor Gö6976 (2 μM) or the PKC activator PMA (1 μM), respectively. (Control, n = 10; U73122, n = 7, ***P < 0.001; Gö6976, n = 11, **P < 0.01; PMA, n = 11, **P < 0.01). (D) Concentration–response curves for cAMP-induced currents in inside-out patches from cells expressing Orco. Data represent maximum mean currents at −60 mV produced under control conditions and with 500 μM GDP-β-S, 10 μM U73122 or 1 μM Gö6976 in the bath. (Control, n = 13; GDP-β-S, n = 17, ***P < 0.001; U73122, n = 16, ***P < 0.001; Gö6976, n = 10, ***P < 0.001). The continuous curves are Hill fits described by EC50 values of 677 pM, 33 nM and 10 nM and Hill coefficients of 0.40, 0.33, and 0.51 for the control, GDP-β-S and U73122, respectively.