Table 1.
Optimization of Reaction Conditions.a
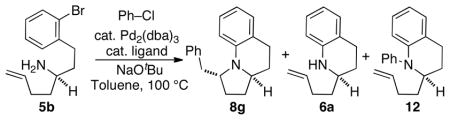 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| entry | ligand | product ratio 8g:6a:12b | |
| 1 |
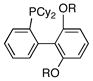
|
R = Me (13) | 14:0:1 |
| 2 | R = iPr | 4:0:1 | |
| 3 |
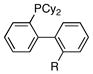
|
R = NMe2 | 3:0:1 |
| 4 | R = Me | 4:0:1 | |
| 5 |
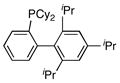
|
(14) | 10:0:1 |
| 6 |
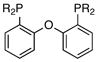
|
R = Ph (4)c | 0:1:0 |
| 7 | R = Cy (15)c | >20:0:1 (63% yield)d | |
| 8 | PCy3•HBF4 | >20:0:1 | |
Conditions: 1.0 equiv 5b, 1.2 equiv PhCl, 2.4 equiv NaOtBu, 1 mol % Pd2(dba)3, 4 mol % ligand, toluene (0.25 M), 100 °C, 5–24 h.
Product ratios were determined by 1H NMR analysis of crude reaction mixtures.
The reaction was conducted using 2 mol % ligand.
The product was isolated with 25:1 dr, although analysis of the crude reaction mixture indicated the product had been formed with 8:1 dr.
