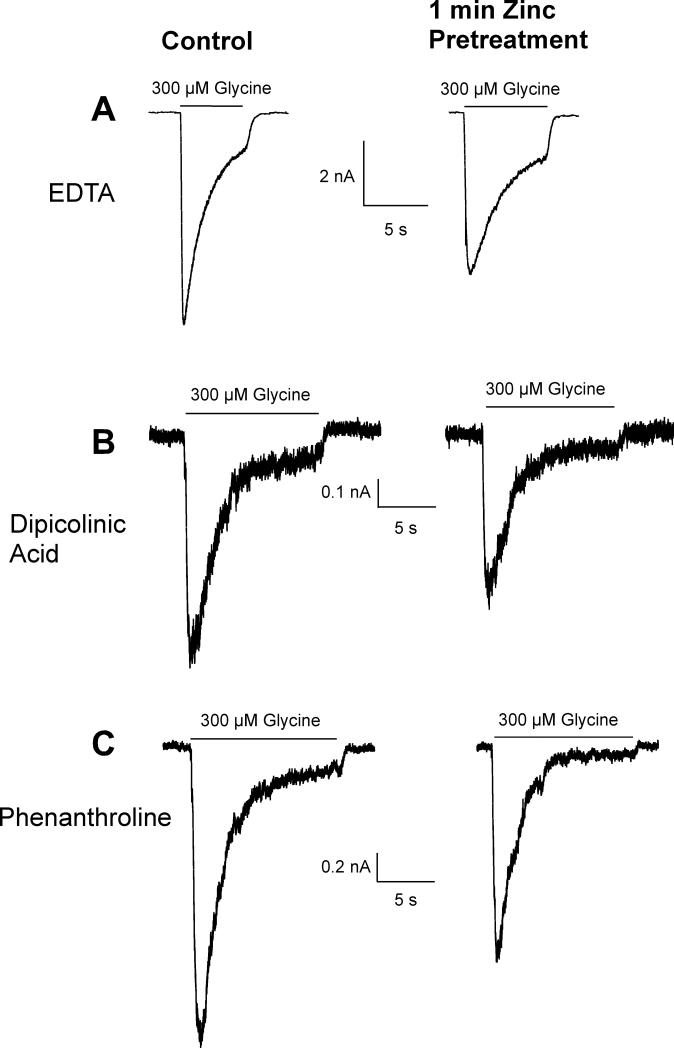
Figure 6.
Intracellular zinc chelation has little effect on the inhibitory actions of extracellular application of 300 μM zinc on glycine-evoked (300 μM) currents. After a 300 μM glycine-evoked control current was recorded, neurons were exposed to 300 μM zinc for 60 seconds and another glycine-evoked current was recorded. Neither 10 mM EDTA (A), nor 100 μM dipicolinic acid (B), nor 100 μM 1,10-phenantroline (C), when applied intracellularly via the recording electrode, were effective at reducing the inhibition of glycine-evoked currents by zinc.