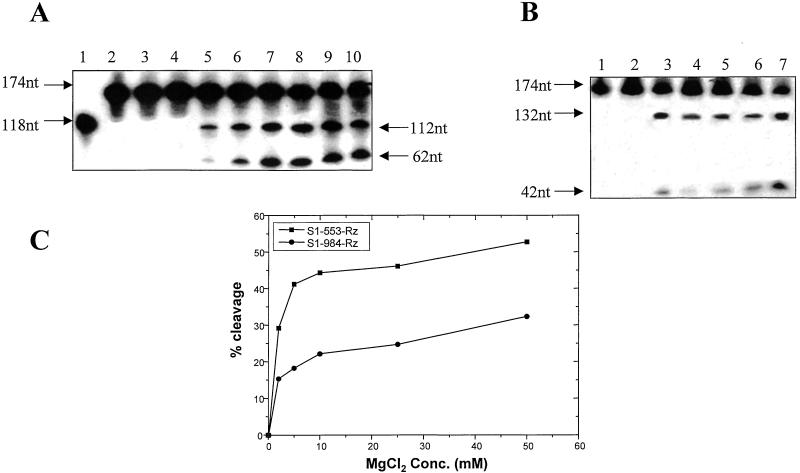
Figure 3.
The effect of varying the concentration of MgCl2 on cleavage efficiency. Synthetic s1 RNA (174 nts long) (A, lane 2 and B, lane 1) was used for the cleavage reaction in equimolar ratio (0.3 pmols) with the two Rzs separately. (A) The results obtained with Rz-553 are shown. Lane 1 depicts the synthesis of Rz-553 as described before. Lane 2 depicts the labeled s1 synthetic transcript that is 174 bases long. No cleavage was observed if the MgCl2 was omitted from the reaction (lane 3) or when it was present at a concentration of 0.1 mM (lane 4). Specific cleavage could be observed at 1 mM MgCl2 (lane 5). The cleavage efficiency increased significantly in the presence of increasing amounts of MgCl2 (lane 6, 3 mM; lane 7, 5 mM; lane 8, 10 mM; lane 9, 25 mM; and lane 10, 50 mM). (B) Lane 1 is same as lane 2 of A. No cleavage was observed in the absence of MgCl2 (lane 2) when equimolar amounts of Rz-984 were used. Lane 3 shows the extent of cleavage in the presence of 2 mM MgCl2. Specific cleavage products were also obtained under simulated physiological conditions (150 mM KCl, pH 7.5, 37°C, 2 mM MgCl2) (lane 4). The cleavage efficiency did not change in the presence of 5 mM (lane 5) or 10 mM MgCl2 (lane 6). Increased cleavage was, however, observed in the presence of 50 mM MgCl2. (C) A comparison of the cleavage efficiency of the two Rzs at varying concentration of MgCl2 is shown. It is evident from the graph that more than 40% cleavage of the target RNA is achieved by Rz-553 in presence of 5 mM MgCl2 as compared with only 20% with Rz-984 under identical experimental conditions. Also note that even in the presence of 50 mM MgCl2 the cleavage reaction did not proceed to completion.