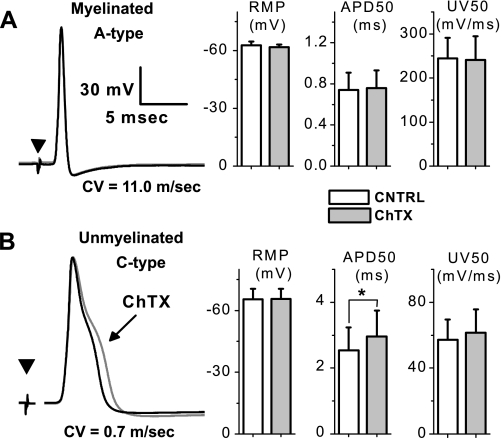
Fig. 3.
Differential effects of charybdotoxin (ChTX) on action potential wave shape using an intact vagal ganglion preparation. Somatic action potentials were evoked through electrical stimulation (▾) of the attached vagus nerve in a myelinated A-type afferent with a conduction velocity (CV) of 11.0 m/s (A) and an unmyelinated C-type afferent with a CV of 0.7 m/s (B). No change in CV, resting membrane potential (RMP), upstroke velocity (UV), and other measures of the action potential wave shape was observed between the control (CNTRL) and ChTX recordings. Differential sensitivity to 100 nM ChTX bath applied to the intact ganglion was most evident in measures of the duration of the nerve evoked action potential duration (APD50; n = 9; *P < 0.05).