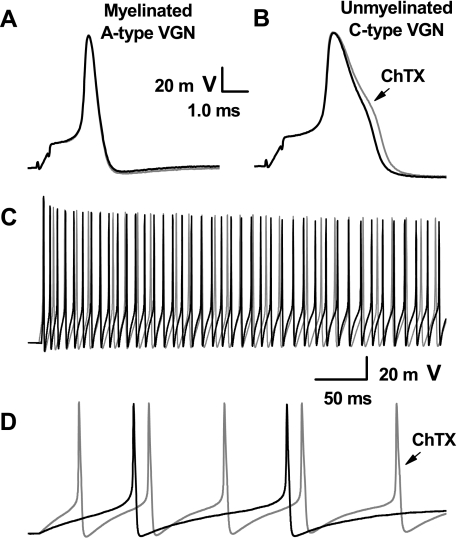
Fig. 4.
Differential effects of ChTX on neuronal excitability using an intact vagal ganglion preparation. With the use of CV as a definitive measure of afferent type, somatic action potentials were elicited by brief current stimulation through the patch electrode. Again, myelinated A-type afferents (A) were unchanged, while action potentials from unmyelinated C-type afferents (B) broadened in response to 100 nM ChTX. Step depolarizing currents elicited repetitive discharge in both types of afferents, but in contrast myelinated A-type (C) showed no significant difference in discharge frequency while unmyelinated C-type afferents (D) were markedly more excitable in the presence of 100 nM ChTX (gray traces). See Table 1 for summary data.