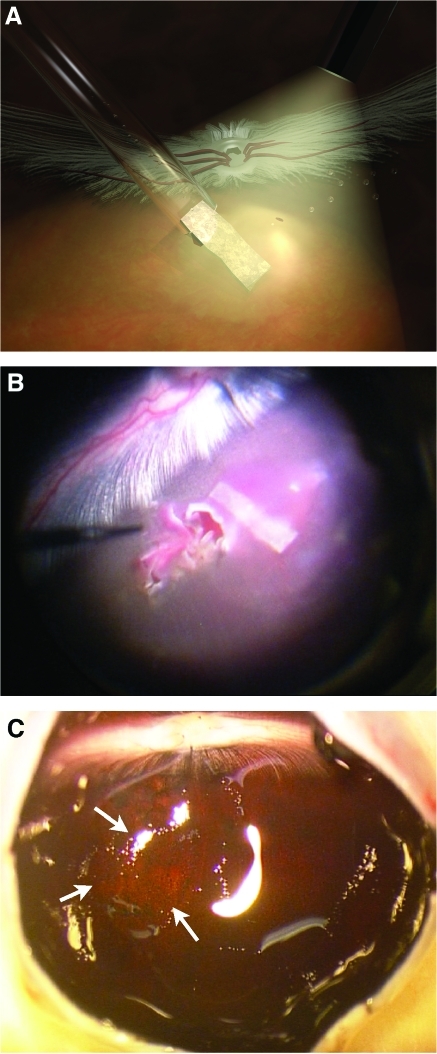
FIG. 2.
The PGS membrane in the subretinal space of rabbit eyes. (A) Illustration of the PGS implantation procedure. After a core vitrectomy including a posterior vitreous detachment, a local neuroretinal detachment has been created by infusing Ames' solution through a retinotomy and into the subretinal space. A second pinpoint retinotomy has been made in the bleb. The PGS membrane, drawn into a siliconized glass capillary, is introduced into the eye, and pushed out into the subretinal space using fluid from an attached syringe. As the membrane enters the subretinal space, the excess fluid escapes through the second retinotomy. (B) Perioperative photograph through the operating microscope. The membrane can be seen as a gray rectangular shape together with a small amount of blood derived from the choroid. (C) Dissection, 28 days after PGS implantation. The retina is attached, and an area with altered choroidal pigmentation is present (arrows). Color images available online at www.liebertonline.com/tea