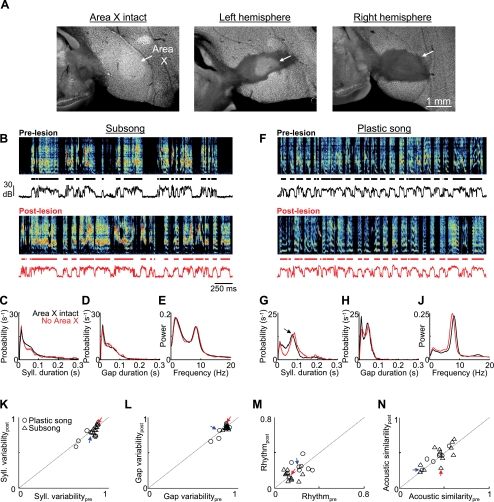
Fig. 2.
Song variability is preserved after Area X lesions. A: histological verification of Area X lesion. In a control bird (left), the boundaries of Area X are readily visible with the Neu-N stain for neuronal cell bodies (see methods). Neuronal labeling reveals bilateral elimination of Area X following injection of the excitotoxin N-methyl-dl-aspartic acid (NMA) into the center of each Area X (see methods). B–E: data from an Area X-lesioned subsong bird. B, top: prelesion song spectrogram of a subsong bird (dph 44). Bottom trace is the song amplitude. Black segments indicate individual syllables. Bottom, spectrogram taken from the first day of singing (dph 46) after bilateral Area X lesions. Note the preservation of variability in the durations of syllables and gaps and in the acoustic structure of syllables. C and D: histograms of syllable (C) and gap (D) durations before (black traces) and after (red traces) the Area X lesion. E: normalized power spectra of the sound amplitudes before and after the lesion. F–J: data from an Area X-lesioned plastic song bird (prelesion song: dph 49, postlesion song: dph 53; histology shown in A) are plotted as in B–E. Note the similarity between pre- and postlesion songs. Arrow in G points to the peak in the syllable duration distribution that is typical in plastic song birds. K–N: population data from Area X lesions in subsong (n = 12) and plastic song (n = 7) birds. K and L: for each bird, the variability in syllable and gap durations was estimated from the entropy of the duration distributions (see methods). Scatterplots show postlesion vs. prelesion syllable (K) and gap (L) duration variability. M: song rhythmicity, computed as the peak of the normalized power spectrum (as in E and J; see methods), for pre- and postlesion song. N: average pairwise spectrogram cross-correlations in pre- and postlesion song. Red and blue arrows point to the data points from the subsong and plastic song birds from B–E and F–J, respectively. Note that none of the measures shown here was significantly affected by Area X lesions.